 he Parapsychologist Ganzfeld Experiment is a fascinating scientific study conducted to explore the phenomenon of extrasensory perception (ESP). This experimental approach aims to provide insights into the potential existence of telepathic communication and psychic abilities. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the Ganzfeld Experiment, its history, methodology, and the intriguing findings that have both fascinated and perplexed researchers and skeptics alike.
he Parapsychologist Ganzfeld Experiment is a fascinating scientific study conducted to explore the phenomenon of extrasensory perception (ESP). This experimental approach aims to provide insights into the potential existence of telepathic communication and psychic abilities. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the Ganzfeld Experiment, its history, methodology, and the intriguing findings that have both fascinated and perplexed researchers and skeptics alike.
The Origins and Evolution of the Ganzfeld Experiment
The Ganzfeld Experiment, developed in the 1970s by parapsychologists, emerged as a means to investigate telepathic and psychic phenomena. The term “Ganzfeld” refers to a technique used to induce a state of mild sensory deprivation, eliminating external stimuli and facilitating a receptive mental state. The experiment draws inspiration from earlier studies in parapsychology and builds upon the belief that certain individuals possess the ability to access information beyond the scope of the traditional senses.
The concept of Ganzfeld experiments can be traced back to the early work of researchers such as Joseph Banks Rhine and Karl Zener, who sought to test the existence of ESP through card-guessing experiments. Over time, the methodology evolved to incorporate the Ganzfeld technique, providing a controlled environment for participants to potentially tap into their extrasensory abilities.
The Ganzfeld Experiment gained wider recognition in the 1980s when it became a prominent component of parapsychological research. Its goal was to provide empirical evidence for telepathy and clairvoyance, which are considered forms of ESP. While the experiment has faced skepticism and criticism, it continues to be conducted in various forms, contributing to ongoing discussions and debates in the field of parapsychology.
Conducting the Ganzfeld Experiment: Methodology and Procedure
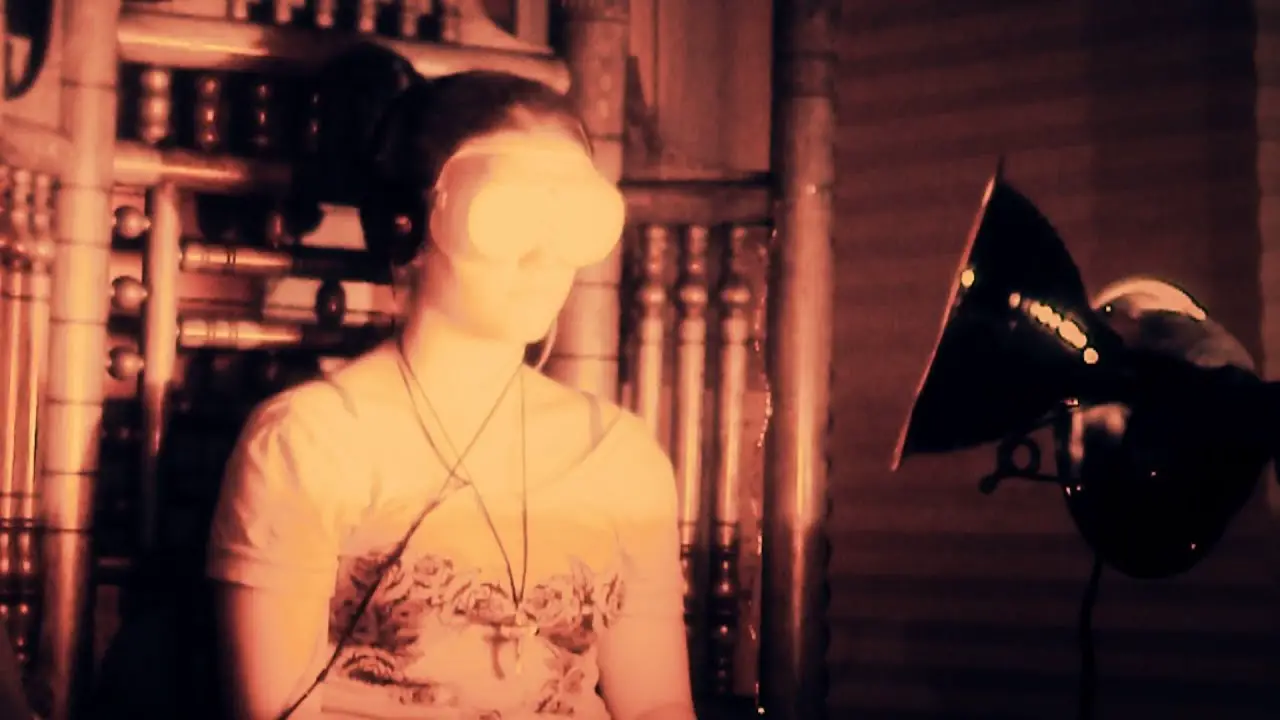
The Ganzfeld Experiment involves a controlled setting where a “sender” and a “receiver” participate. The sender is typically someone who views a randomly selected target image or video, while the receiver is in a Ganzfeld state, experiencing sensory isolation. The receiver’s task is to describe or sketch the target image or video without any direct sensory input.
The procedure typically follows a standardized protocol. The receiver is placed in a relaxed state, often through the use of white noise, soft lighting, and half ping-pong balls placed over their eyes. This setup aims to reduce external sensory stimulation and create a receptive state for potential extrasensory perception.
During the Ganzfeld session, the receiver is encouraged to describe or sketch any impressions, images, thoughts, or feelings that arise. The sender, who has been exposed to a specific target, later reveals the target image or video to compare it with the receiver’s description. Statistical analysis is employed to assess the accuracy of the receiver’s perceptions and determine if the results exceed chance expectations.
Interpreting the Findings: Controversies and Criticisms
The Ganzfeld Experiment has yielded a range of results, with some studies suggesting statistically significant outcomes supporting the existence of telepathy or ESP, while others have found no conclusive evidence. Critics argue that methodological flaws, experimenter bias, and the potential for sensory leakage or unintentional cues may undermine the validity of the findings. Additionally, the subjective nature of the receiver’s experiences introduces challenges in quantifying and replicating results.
Skeptics also point to the concept of the file-drawer problem, which suggests that negative or inconclusive results may go unpublished, skewing the overall perception of the experiment’s success rate. The scientific community continues to debate the replicability and robustness of the Ganzfeld Experiment, calling for rigorous controls, larger sample sizes, and independent replication to strengthen the findings.
While the Ganzfeld Experiment has faced criticism, proponents argue that statistically significant positive outcomes in some studies warrant further investigation. They emphasize the need for an open-minded approach and a willingness to explore unconventional phenomena that challenge our understanding of consciousness and human potential.
The Legacy and Future of the Ganzfeld Experiment
The Ganzfeld Experiment has left an indelible mark on the field of parapsychology and continues to spark interest and intrigue. Despite ongoing debates and varying interpretations of its findings, the experiment has prompted scientific inquiry into the mysteries of consciousness, perception, and the potential for human psychic abilities.
Moving forward, researchers advocate for the continued exploration of the Ganzfeld Experiment and the refinement of experimental protocols to address methodological concerns. Advances in technology and statistical analysis offer promising avenues for enhancing the experiment’s reliability and reducing potential biases.
Ultimately, the Ganzfeld Experiment remains a subject of fascination and controversy, representing the intersection of science and the paranormal. Its impact extends beyond the laboratory, captivating the imagination of both believers and skeptics, as we seek to unravel the mysteries of the human mind and explore the boundaries of our perceptual capabilities.
The Parapsychologist Ganzfeld Experiment provides a unique platform for investigating the potential existence of telepathic communication and psychic phenomena. While the experiment has faced criticisms and controversies, its enduring legacy underscores the human fascination with unlocking the mysteries of extrasensory perception. As research progresses and scientific methodologies evolve, the Ganzfeld Experiment continues to contribute to our understanding of consciousness, human potential, and the enigmatic realms that lie beyond our traditional senses.
Avid Writer with invaluable knowledge of Humanity!
Upcoming historian with over 30 million views online.
“You make your own life.”





