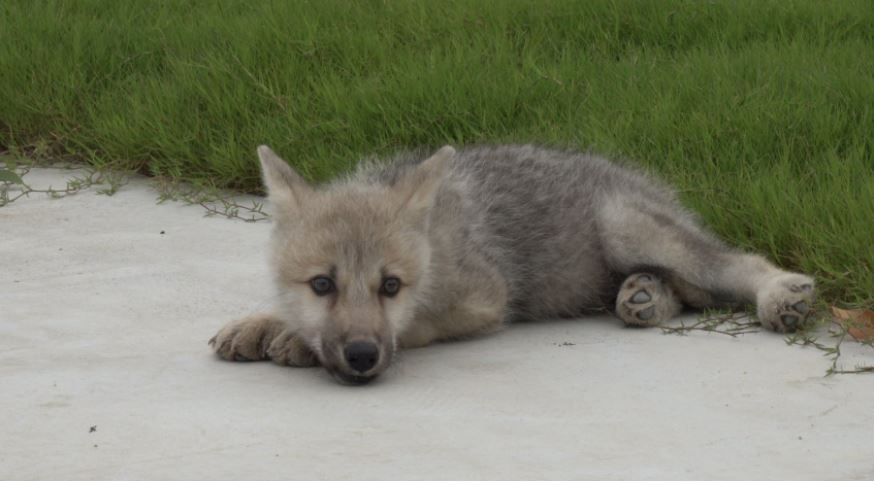
 a groundbreaking scientific achievement, the world’s first cloned Arctic wolf recently marked a significant milestone—100 days of life. This remarkable event represents a major breakthrough in the field of cloning and conservation efforts. Inspired by the article “World’s first cloned Arctic wolf is now 100 days old” published by Freethink, this article will delve into the fascinating journey of the cloned Arctic wolf, explore the implications of this scientific feat, and discuss the potential impact on wildlife conservation.
a groundbreaking scientific achievement, the world’s first cloned Arctic wolf recently marked a significant milestone—100 days of life. This remarkable event represents a major breakthrough in the field of cloning and conservation efforts. Inspired by the article “World’s first cloned Arctic wolf is now 100 days old” published by Freethink, this article will delve into the fascinating journey of the cloned Arctic wolf, explore the implications of this scientific feat, and discuss the potential impact on wildlife conservation.
Cloning the Arctic Wolf: A Triumph of Science
The birth of the cloned Arctic wolf, a result of the innovative work of scientists, has opened new avenues for genetic preservation and species conservation. Through the use of advanced cloning techniques, a viable embryo was created using genetic material from a donor Arctic wolf, marking the dawn of a new era in wildlife cloning.
The successful cloning of the Arctic wolf was not without its hurdles. Scientists had to overcome numerous technological challenges, including the extraction and manipulation of genetic material, the development of a healthy cloned embryo, and the successful implantation into a surrogate wolf. The achievement of producing a viable cloned Arctic wolf signifies significant advancements in cloning technology and reproductive biology.
Cloning the Arctic wolf holds immense promise for preserving the genetic diversity of endangered or extinct species. By recreating the genetic blueprint of a species, scientists can potentially resurrect populations that have been severely depleted or entirely wiped out. This advancement opens up new possibilities for conservation efforts and the restoration of fragile ecosystems.
Ethical Considerations and Conservation Implications
The cloning of animals, including the Arctic wolf, raises important ethical questions. Critics argue that cloning interferes with the natural order of reproduction and may compromise the genetic diversity necessary for long-term survival. It is crucial for scientists and policymakers to carefully consider the ethical implications of cloning and establish guidelines to ensure responsible and sustainable practices.
Cloning technologies have the potential to complement existing conservation strategies, particularly in cases where traditional breeding programs face challenges. The ability to create genetic replicas of rare or endangered species offers an additional tool for conservationists to safeguard biodiversity and prevent the irreversible loss of crucial genetic resources.
Public perception plays a vital role in shaping the acceptance and implementation of cloning technologies in wildlife conservation. Open dialogue, public education, and transparent communication from scientists and conservation organizations are essential to address concerns, foster understanding, and build trust. A collaborative approach involving scientists, policymakers, and the public is crucial to ensure responsible and ethical use of cloning technologies in the realm of wildlife conservation.
The Future of Cloning and Conservation
The successful cloning of the Arctic wolf marks a significant milestone, but there is still much to learn and explore. Continued research and advancements in cloning techniques will likely enhance success rates, improve efficiency, and reduce potential risks associated with the process. This progress paves the way for future endeavors in wildlife cloning and conservation.
The cloning of the Arctic wolf opens up possibilities for cloning other endangered species, providing a glimmer of hope for their survival. By applying similar techniques to other at-risk species, scientists can contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and help reverse the negative impacts of human activities, habitat loss, and climate change.
While cloning technologies offer promising avenues for conservation, it is crucial to adopt a holistic approach that combines cloning with other conservation strategies. Habitat protection, wildlife management, and public awareness campaigns should work in harmony with cloning efforts to ensure the long-term viability and well-being of species and ecosystems.
The world’s first cloned Arctic wolf reaching the milestone of 100 days of life signifies a remarkable achievement in the realm of cloning and wildlife conservation. This scientific breakthrough opens up new possibilities for genetic preservation, species revival, and biodiversity conservation. However, ethical considerations, public perception, and the integration of cloning technologies into comprehensive conservation strategies are critical for responsible and effective implementation. As we continue to explore the frontiers of cloning and conservation, we must strike a delicate balance between scientific progress, ethical considerations, and the preservation of the natural world.
Avid Writer with invaluable knowledge of Humanity!
Upcoming historian with over 30 million views online.
“You make your own life.”





