Overview
Introduction to the Roman Empire
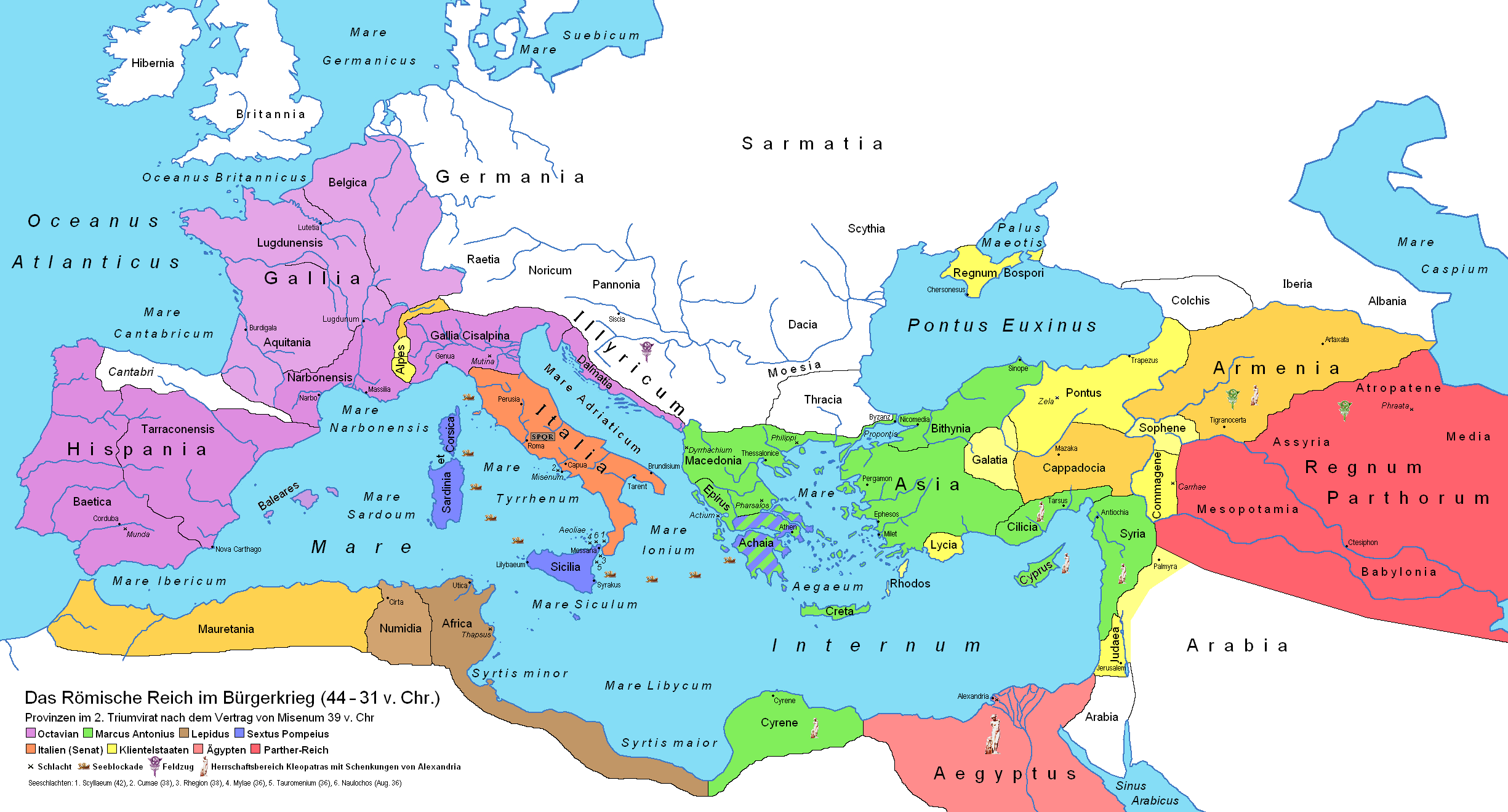
The Roman Empire, one of the most powerful and influential civilizations in history, spanned over a thousand years, from 27 BC to 476 AD. It began as a small city-state in Italy and grew to encompass vast territories, stretching from Britain in the west to Egypt in the east. The empire’s rise to dominance was marked by a series of military conquests, effective governance, and the development of a sophisticated infrastructure. The Romans built an extensive road network, aqueducts, and impressive architectural structures, such as the Colosseum and the Pantheon. These achievements not only facilitated trade and communication but also showcased the grandeur and power of the empire. The Roman Empire’s expansion and consolidation of power laid the foundation for its eventual decline, as it faced numerous challenges, both internal and external, that would ultimately contribute to its fall.
Expansion and Consolidation of Power
During the expansion and consolidation of power, the Roman Empire experienced a period of significant growth and stability. The empire’s territorial conquests allowed it to expand its influence and establish control over vast regions. The Roman military played a crucial role in this process, with its highly disciplined and well-trained soldiers dominating the battlefield. The empire’s effective governance and administration also contributed to its success. The Roman government was characterized by a well-structured bureaucracy that efficiently managed the affairs of the empire. This allowed for the smooth administration of conquered territories and the integration of diverse cultures into the Roman way of life. Furthermore, the empire invested heavily in infrastructure development, constructing an extensive network of roads, bridges, and aqueducts. These infrastructure projects facilitated trade and communication within the empire, further strengthening its position. Overall, the expansion and consolidation of power marked a crucial phase in the Roman Empire’s history, laying the foundation for its future dominance and influence.
Socio-Political Structure of the Empire
The socio-political structure of the Roman Empire was a complex system that played a crucial role in the rise and fall of the empire. At the top of the hierarchy was the emperor, who held absolute power and was considered divine. Below the emperor were the aristocracy and the senatorial class, who held significant political influence and wealth. The lower classes, including the common people and slaves, made up the majority of the population and had limited rights and freedoms. The empire was governed by a combination of central and local administrations, with provincial governors appointed by the emperor. The Roman legal system, based on the principles of justice and fairness, provided a framework for maintaining order and resolving disputes. The socio-political structure of the empire also influenced the cultural and intellectual life of its citizens. Memoirs and novels in Prague were written by authors who drew inspiration from the rich history and diverse population of the Roman Empire. These literary works provided insights into the social, political, and economic aspects of Roman society. Overall, the socio-political structure of the Roman Empire was a complex and dynamic system that shaped the course of its history.
Causes of the Roman Empire’s Rise

Military Strength and Conquests
The military strength and conquests of the Roman Empire played a crucial role in its rise and expansion. The Roman army was known for its discipline, organization, and tactical superiority, which allowed it to conquer vast territories and establish dominance over various regions. The empire’s military prowess was further enhanced by its ability to adapt and incorporate the military strategies and technologies of the conquered peoples. This not only increased the empire’s military capabilities but also facilitated the assimilation of diverse cultures into the Roman way of life. The Roman army’s conquests not only expanded the empire’s territorial boundaries but also brought immense wealth and resources, which fueled its economic growth and prosperity. The influence of Cicero on Roman law was also significant during this period, as his legal theories and writings shaped the development of the Roman legal system, laying the foundation for future legal principles and practices.
Effective Governance and Administration
One of the key factors contributing to the rise of the Roman Empire was its effective governance and administration. The empire was governed by a well-structured system that allowed for efficient decision-making and coordination of resources. The Roman government established a centralized bureaucracy that oversaw various aspects of administration, including taxation, law enforcement, and public works. This system ensured that the empire was effectively governed and that its policies were implemented across the vast territories it controlled. Additionally, the Roman Empire had a strong military that played a crucial role in maintaining order and protecting the empire’s borders. The army was well-disciplined and highly organized, allowing the empire to successfully defend itself against external threats. Furthermore, the Roman Empire invested heavily in infrastructure development, constructing an extensive network of roads, aqueducts, and buildings. These infrastructure projects not only facilitated trade and communication but also showcased the empire’s power and grandeur. However, despite its effective governance and administration, the Roman Empire faced numerous challenges and eventually experienced a decline.
Infrastructure Development
Infrastructure development played a crucial role in the rise and prosperity of the Roman Empire. The Romans were renowned for their advanced engineering skills and the construction of impressive public works. They built an extensive network of roads that connected the far reaches of the empire, facilitating trade, communication, and the movement of troops. These roads were meticulously constructed with durable materials such as stone and concrete, ensuring their longevity. In addition to roads, the Romans also constructed aqueducts to supply water to their cities, bridges to span rivers and valleys, and sewers to maintain sanitation. The construction of these infrastructure projects not only improved the quality of life for the Roman citizens but also facilitated the efficient administration and governance of the empire. The legacy of Roman infrastructure development can still be seen today in the remnants of ancient structures that have stood the test of time.
Challenges and Decline of the Roman Empire
Barbarian Invasions and External Threats
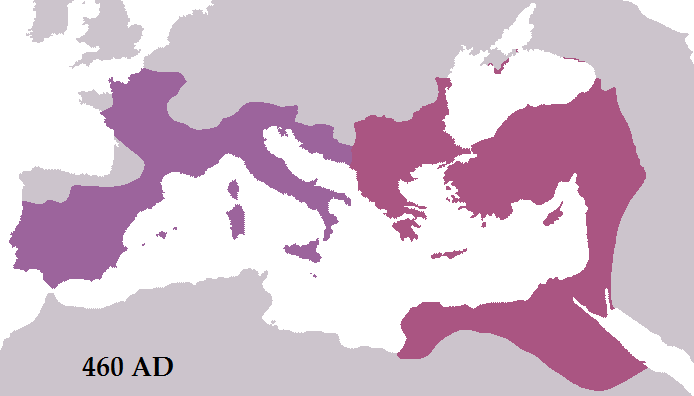
The Barbarian invasions and external threats played a significant role in the decline of the Roman Empire. As the empire expanded, it encountered various barbarian tribes such as the Visigoths, Ostrogoths, Vandals, and Huns, who posed a constant threat to the Roman borders. These barbarian tribes, driven by a desire for land and resources, launched numerous invasions, putting immense pressure on the already weakened Roman military. The Roman Empire faced major defeats, such as the sack of Rome by the Visigoths in 410 CE and the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 CE at the hands of the Germanic chieftain Odoacer. These invasions not only weakened the empire’s military strength but also disrupted trade routes and caused economic instability. The constant warfare and the need to defend against external threats drained the empire’s resources and diverted attention from internal issues. The inability to effectively repel these invasions and protect its borders ultimately contributed to the decline and fall of the once mighty Roman Empire.
Internal Political Instability
The internal political instability of the Roman Empire was a major factor in its decline. Power struggles and corruption within the ruling elite often led to frequent changes in leadership and weakened central authority. The assassination of emperors and civil wars further destabilized the empire. Additionally, the influence of the military in politics created a volatile environment where loyalties shifted and loyal generals could easily become rival claimants to the throne. This constant state of political turmoil made it difficult for the empire to effectively govern itself and respond to external threats. As a result, the Roman Empire became vulnerable to barbarian invasions and struggled to maintain control over its vast territories. The internal political instability also had social repercussions, with economic inequality and social unrest becoming more prevalent. These factors contributed to the eventual collapse of the Roman Empire.
Economic Crisis and Decline
The economic crisis and decline of the Roman Empire was a significant factor in its downfall. Cease comparing the West to Rome. The empire faced numerous challenges that contributed to its economic decline and eventual collapse. One major factor was the increasing reliance on slave labor, which led to a decline in productivity and innovation. Additionally, the empire’s vast territorial expansion strained its resources and led to high taxation, which burdened the economy and hindered economic growth. Furthermore, the constant warfare and military expenses drained the treasury and further weakened the economy. The decline of trade and the disruption of long-distance commerce also played a role in the economic crisis. The collapse of the Roman currency system and the devaluation of the denarius further exacerbated the economic decline. These economic challenges, combined with other internal and external factors, ultimately led to the fall of the Roman Empire.
Conclusion

Legacy of the Roman Empire
The legacy of the Roman Empire is far-reaching and has left an indelible mark on Western civilization. One of the most significant contributions of the empire is its legal system, which formed the basis for modern legal principles and institutions. The Romans introduced the concept of citizenship, providing a framework for the rights and responsibilities of individuals within a society. Additionally, the empire’s architectural achievements, such as the construction of aqueducts, roads, and monumental structures like the Colosseum and the Pantheon, demonstrated their engineering prowess and continue to inspire awe today. The Romans also made significant advancements in literature and philosophy, with notable figures like Cicero and Seneca shaping intellectual thought. Furthermore, the spread of Christianity within the empire and its eventual adoption as the state religion had a profound impact on the development of European culture and religious practices. The Roman Empire’s legacy can be seen in various aspects of modern society, including government, law, architecture, language, and religion.
Lessons Learned from its Rise and Fall
The rise and fall of the Roman Empire offers valuable lessons for understanding the complexities of empire-building and the factors that contribute to its ultimate demise. One of the key lessons learned from the empire’s history is the importance of strong leadership and effective succession planning. The death of Augustus marked a significant turning point in the empire’s trajectory. Despite his remarkable achievements in consolidating power and establishing a stable government, the lack of a clear and successful succession plan after his death led to a period of political instability and internal conflict. This highlights the critical role of leadership and the need for a smooth transition of power in maintaining the stability and longevity of an empire. Furthermore, the decline of the Roman Empire also underscores the importance of economic stability and the dangers of overreliance on conquest and expansion. The empire’s vast territorial acquisitions and military campaigns placed a strain on its resources, leading to economic hardships and ultimately contributing to its downfall. This serves as a reminder of the need for balanced economic policies and sustainable growth strategies in order to prevent the collapse of an empire. Overall, the rise and fall of the Roman Empire serve as a cautionary tale, reminding us of the complex interplay of political, economic, and social factors that shape the destiny of empires.
Impact on Western Civilization
The impact of the Roman Empire on Western Civilization is immeasurable. The history of Ancient Rome has left an indelible mark on the development of Western societies in various aspects. One of the most significant contributions of the Roman Empire is its legal system, which laid the foundation for modern legal principles and concepts. The Roman legal system, with its emphasis on the rule of law and the protection of individual rights, has greatly influenced the legal systems of many Western countries. Additionally, the Roman Empire’s architectural and engineering achievements continue to inspire and awe people to this day. The grandeur and sophistication of structures such as the Colosseum, the Pantheon, and the aqueducts showcase the engineering prowess of the Romans. These architectural marvels have served as models for countless buildings and structures throughout history. Furthermore, the Roman Empire’s influence on language and literature cannot be overstated. Latin, the language of the Romans, has shaped the development of many European languages, including English. Many English words and phrases have their roots in Latin, and the study of Latin remains an important part of education in many Western countries. The literary works of ancient Roman writers such as Virgil, Cicero, and Ovid have also had a profound impact on Western literature. Their works have been studied, translated, and celebrated for centuries, influencing the literary traditions of subsequent generations. In conclusion, the Roman Empire’s impact on Western Civilization is multifaceted and enduring, encompassing areas such as law, architecture, language, and literature. The legacy of Ancient Rome continues to shape and inspire Western societies, serving as a reminder of the remarkable achievements and the tumultuous history of the Roman Empire.
Avid Writer with invaluable knowledge of Humanity!
Upcoming historian with over 30 million views online.
“You make your own life.”