Overview
Introduction to the Silk Road
The Silk Road was an extensive network of ancient trade routes that connected East Asia with the Mediterranean world, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. It played a crucial role in the growth and development of trade in ancient India, as it provided a vital link between the Indian subcontinent and other regions. The Silk Road was not just a physical route, but also a platform for cultural exchange and intellectual discourse. Merchants, scholars, and travelers from diverse backgrounds traversed these routes, bringing with them their unique traditions, beliefs, and knowledge. This intermingling of cultures along the Silk Road led to the emergence of a cosmopolitan society where ideas, art, and technology flourished.
Historical significance of the Silk Road
The Silk Road holds immense historical significance as it facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between the East and the West. This ancient trade route played a pivotal role in shaping the course of history by connecting civilizations and fostering cross-cultural interactions. The Silk Road not only facilitated the trade of valuable commodities such as silk, spices, and precious metals, but it also served as a conduit for the transmission of religious and philosophical ideas. Buddhism, for example, spread from India to China along the Silk Road, transforming the spiritual landscape of East Asia. Additionally, the Silk Road served as a platform for the exchange of artistic and architectural influences, resulting in the fusion of different artistic styles and the creation of unique cultural expressions. The intricate carvings found in Buddhist caves along the Silk Road, such as the Mogao Caves in Dunhuang, exemplify the rich artistic heritage that emerged from this cultural exchange. Furthermore, the Silk Road played a crucial role in the dissemination of culinary traditions, with new ingredients and cooking techniques being introduced and adopted along the route. The fusion of Eastern and Western culinary practices gave rise to a diverse and vibrant gastronomic landscape that continues to influence cuisines around the world. The historical significance of the Silk Road lies not only in its economic impact but also in its role as a catalyst for cultural exchange and the spread of knowledge.
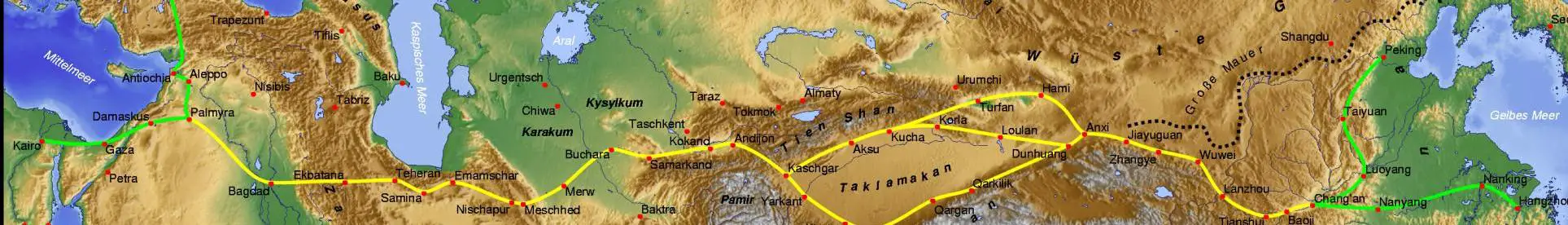
Major trade routes and destinations
The Silk Road was a vast network of trade routes that connected East Asia with the Mediterranean world, allowing for the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. The main routes of the Silk Road included the Northern Route, which passed through Central Asia and connected China with the cities of Samarkand and Bukhara. Another important route was the Southern Route, which ran through the Indian subcontinent and linked China with the ports of India and the Persian Gulf. Additionally, the Maritime Route connected the Mediterranean with East Asia via sea, allowing for the transport of goods such as silk, spices, and precious metals. Along these routes, there were various significant destinations where trade flourished and cultural exchange took place. One such destination was Kostobe’s Heritage, a bustling city known for its vibrant markets and diverse population. Merchants from different parts of the world gathered here to trade goods and share ideas, resulting in a rich blend of cultures and traditions. The city’s strategic location made it a hub for the exchange of goods from both the East and the West, further enhancing its importance as a major trading center on the Silk Road.
Cultural Exchange along the Silk Road

Religious and philosophical ideas
Religious and philosophical ideas played a significant role in the cultural exchange along the Silk Road. The Silk Road served as a conduit for the spread of various religious and philosophical beliefs, including Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, and Confucianism. These belief systems not only influenced the spiritual lives of the people along the Silk Road but also shaped their social, political, and cultural practices. The exchange of ideas and beliefs led to the development of new religious and philosophical schools of thought, as well as the synthesis of different traditions. For example, the interaction between Buddhism and Taoism resulted in the formation of a unique blend known as Zen Buddhism. The Silk Road was not only a physical trade route but also a platform for intellectual and spiritual exchange, fostering a rich tapestry of ideas and philosophies.
Art and architecture
Art and architecture played a significant role in the cultural exchange along the Silk Road. The diverse range of artistic styles and architectural marvels found along the trade routes showcased the blending of different cultures and traditions. Legendary tales of silk and its production techniques were depicted in intricate silk paintings and tapestries, highlighting the importance of this luxurious fabric in the trade network. Buddhist cave temples, such as the Mogao Caves in Dunhuang, China, featured breathtaking murals and sculptures that reflected the influence of Indian and Central Asian artistic traditions. The Silk Road also facilitated the spread of architectural styles, with examples like the Buddhist stupas in Gandhara displaying a fusion of Greek, Persian, and Indian elements. These artistic and architectural exchanges not only enriched the visual landscape of the Silk Road but also fostered cross-cultural understanding and appreciation.
Cuisine and culinary traditions
Cuisine and culinary traditions along the Silk Road were incredibly diverse, reflecting the rich cultural exchange that took place along the ancient trade routes. The Silk Road served as a melting pot of flavors, with spices, ingredients, and cooking techniques being shared and adapted by different cultures. English traders, for example, introduced new ingredients such as tea and spices like cinnamon and nutmeg to the Silk Road. These additions greatly influenced the culinary traditions of the regions they passed through, resulting in the creation of unique and flavorful dishes. The Silk Road also facilitated the spread of cooking techniques, with methods such as stir-frying and steaming being adopted by various cultures. The exchange of culinary knowledge not only enriched the food culture of the Silk Road, but also had a lasting impact on global cuisine, as many of these culinary traditions continue to be enjoyed and celebrated today.
Technological Innovations and Knowledge Transfer

Silk production and sericulture
Silk production and sericulture played a crucial role in the cultural exchange along the Silk Road. The intricate process of silk production originated in ancient China and eventually spread to other regions along the trade routes. Silk, known for its luxurious texture and vibrant colors, became highly sought after by merchants and nobles alike. The silk industry not only facilitated economic prosperity but also fostered cultural exchange between East and West. Through the trade of silk, ideas, technologies, and artistic influences were exchanged, shaping the development of various civilizations. The advancement of sericulture techniques and the establishment of silk production centers contributed to the growth of cities and the formation of new cultural hubs. China’s future role on the global stage was greatly influenced by its dominance in silk production and trade.
Medicine and healing practices
Medicine and healing practices along the Silk Road were diverse and influenced by various cultures and traditions. The exchange of knowledge and techniques in medicine played a crucial role in the development of medical practices in different regions. Herbal medicine was widely practiced, with different plants and herbs used for treating various ailments. Traditional Chinese medicine, with its emphasis on balancing the body’s energy, was also prominent along the Silk Road. Acupuncture and moxibustion were popular methods used for healing and pain relief. The Indian practice of Ayurveda also had a significant impact, with its holistic approach to health and well-being. The Silk Road facilitated the spread of medical knowledge, allowing for the exchange of ideas and the development of new treatments and therapies.
Mathematics and astronomy
Mathematics and astronomy were two fields that greatly benefited from the cultural exchange along the Silk Road. The exchange of knowledge and ideas allowed for advancements in both disciplines, leading to significant contributions to our understanding of the universe and the development of mathematical concepts. Mathematicians from different regions shared their techniques and discoveries, leading to the spread of mathematical knowledge across cultures. Astronomers also benefited from the exchange, as they were able to observe celestial phenomena from various locations along the Silk Road, providing a broader perspective on the stars and planets. This cross-cultural exchange of mathematical and astronomical knowledge laid the foundation for future developments in these fields.
Legacy and Impact of the Silk Road

Spread of languages and writing systems
The Silk Road played a crucial role in the spread of languages and writing systems, facilitating cultural exchange and communication across vast distances. As traders, scholars, and travelers journeyed along the Silk Road, they carried with them not only goods but also ideas and knowledge. One notable example is the transmission of writing systems from East Asia to Europe. The invention of paper in China allowed for the development and dissemination of written texts, which eventually reached Europe through trade routes. This exchange of writing systems enabled the spread of literacy and the preservation of historical records. Additionally, the Silk Road fostered the exchange of languages, leading to the emergence of new dialects and the enrichment of existing ones. The interaction between different cultures along the Silk Road contributed to the development of a diverse linguistic landscape, with influences from various regions and civilizations.
Influence on global trade and economy
The Silk Road had a profound influence on global trade and economy. It facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between East and West, creating a network of interconnected economies. The trade routes of the Silk Road allowed for the flow of valuable commodities such as silk, spices, and precious metals, which stimulated economic growth and prosperity. Additionally, the Silk Road played a crucial role in the development of commercial practices, including the establishment of trade routes, the use of standardized currencies, and the introduction of credit systems. This exchange of goods and knowledge not only enriched the economies of the regions along the Silk Road but also had a lasting impact on global trade patterns and the development of international commerce. The legacy of the Silk Road continues to shape the modern global economy, as it paved the way for the establishment of trade routes and cultural exchange that transcended geographical boundaries.
Revival of the Silk Road in modern times
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the revival of the Silk Road trade routes. This renewed enthusiasm can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the Silk Road trade routes were not only about the exchange of goods, but also about the exchange of ideas, cultures, and knowledge. The revival of these routes has the potential to foster a deeper understanding and appreciation of the diverse cultures and traditions that once thrived along the ancient trade routes. Secondly, the Silk Road trade routes were instrumental in the development of global trade and economy. The revival of these routes can open up new opportunities for trade and economic growth, particularly in the regions that were historically connected by the Silk Road. Lastly, the revival of the Silk Road trade routes can serve as a catalyst for cooperation and collaboration among countries and regions. By reconnecting the ancient trade routes, countries can work together to address common challenges and promote peace and stability in the region. Overall, the revival of the Silk Road trade routes holds immense potential in terms of cultural exchange, economic development, and regional cooperation.
Avid Writer with invaluable knowledge of Humanity!
Upcoming historian with over 30 million views online.
“You make your own life.”