Overview
Introduction to the Silk Road
The Silk Road was an ancient network of trade routes that connected the East and West. It played a crucial role in facilitating cultural exchange, economic development, and political interactions between different civilizations. The term ‘Silk Road’ was coined by the German geographer Ferdinand von Richthofen in the late 19th century, referring to the lucrative trade in silk from China to the Mediterranean region. However, the Silk Road was much more than a mere trade route. It was a complex web of interconnected routes that spanned over 6,000 kilometers, traversing diverse terrains and linking various civilizations. The Silk Road was not only a physical route but also a conduit for the exchange of ideas, knowledge, religions, and philosophies. It fostered a rich cultural exchange between the East and West, leaving a lasting impact on the development of human civilization.
Historical significance of the Silk Road
The Silk Road was not just a trade route, but a fabric connecting East and West. It played a crucial role in shaping the history of the world by facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between the two regions. The significance of the Silk Road goes beyond economic benefits; it fostered a sense of interconnectedness and promoted cultural exchange. Through this ancient network of routes, people from different civilizations came into contact with each other, leading to the spread of ideas, knowledge, and innovations. The Silk Road became a melting pot of diverse cultures, religions, and philosophies, which influenced the development of art, architecture, and even political systems. It served as a bridge between civilizations, allowing the transmission of goods, technologies, and ideologies that transformed societies along its path.
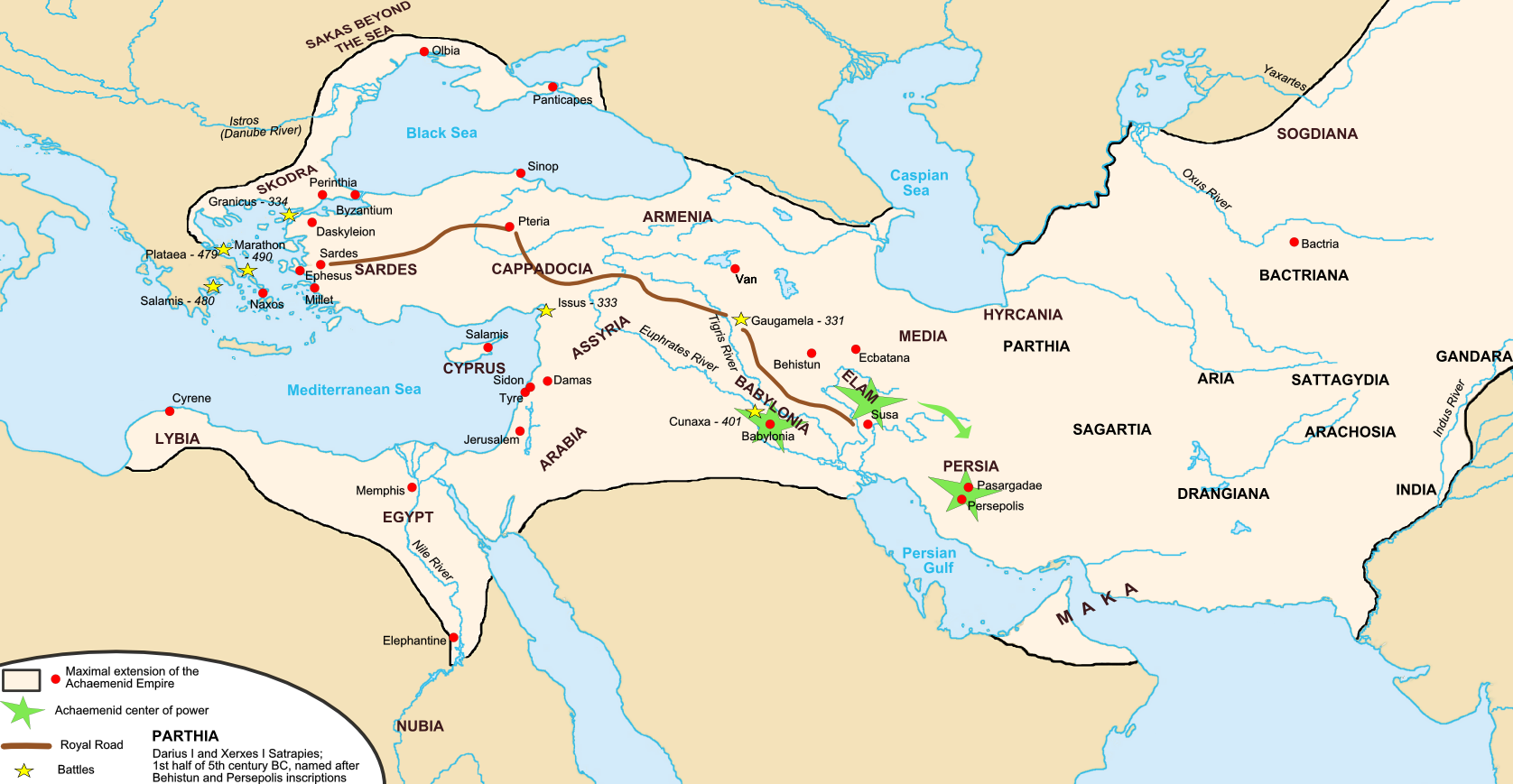
Trade routes and key players
The Silk Road was a vast network of trade routes that connected the East and the West. It spanned thousands of miles, crossing multiple countries and regions. The key players in this intricate web of commerce were not only merchants, but also governments, nomadic tribes, and religious institutions. These various entities played a crucial role in facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures along the Silk Road. They established trading posts, caravanserais, and markets where merchants from different regions could meet and conduct business. The Silk Road was not just a single route, but rather a network of interconnected routes that branched out in different directions, allowing for the flow of goods and people. This extensive trade network enabled the exchange of commodities such as silk, spices, precious metals, and exotic goods. It also facilitated the transmission of knowledge, technologies, and religious beliefs. The Silk Road was a dynamic and vibrant hub of economic and cultural activity, shaping the history and development of civilizations in both the East and the West.
Cultural Exchange

Spread of ideas and knowledge
The Silk Road served as a vital conduit for the exchange of ideas and knowledge between the East and the West. It facilitated the transmission of various cultural, scientific, and technological advancements, fostering a rich intellectual environment that transcended geographical boundaries. One notable example of this exchange is the spread of Buddhism from India to China and other parts of Asia. Buddhist monks and scholars traveled along the Silk Road, carrying scriptures and teachings, which greatly influenced the religious and philosophical landscape of the region. The Silk Road also played a significant role in the dissemination of scientific knowledge, particularly in the fields of astronomy, mathematics, and medicine. Scholars from different civilizations shared their discoveries and theories, contributing to the advancement of human understanding. The exchange of ideas and knowledge along the Silk Road was not limited to academia; it also encompassed artistic and cultural expressions. Artists, artisans, and craftsmen from various cultures interacted and shared techniques, resulting in the fusion of different artistic styles and the emergence of new forms of artistic expression. The Silk Road truly served as a bridge between East and West, fostering a vibrant exchange of ideas and knowledge that shaped the development of civilizations across continents.
Artistic and architectural influences
The Silk Road served as a conduit for the exchange of artistic and architectural influences between East and West. The flow of ideas and creativity along the trade routes resulted in a fusion of styles and techniques that shaped the cultural landscape of both regions. One notable example is the influence of Central Asian architecture on the development of Islamic architecture. The intricate geometric patterns and domed structures of Central Asian mosques and mausoleums inspired the design of iconic Islamic architectural landmarks such as the Taj Mahal in India and the Blue Mosque in Turkey. Similarly, the Silk Road facilitated the spread of artistic techniques like ceramics and silk weaving. The delicate porcelain of China and the vibrant silk fabrics of Persia captivated the imaginations of artists and craftsmen, leading to the creation of exquisite works of art that showcased the skill and creativity of both cultures. The Silk Road truly served as a melting pot of artistic and architectural influences, fostering cross-cultural exchange and leaving a lasting legacy of beauty and innovation.
Religious and philosophical exchange
The Silk Road played a crucial role in facilitating the exchange of religious and philosophical ideas between the East and the West. It served as a conduit for the spread of religions such as Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, and Hinduism. The interaction between different cultures and belief systems along the Silk Road led to the development of syncretic religious practices and the blending of different philosophical traditions. For example, the teachings of Buddhism from India influenced the development of Zen Buddhism in China and Japan. Similarly, the introduction of Greek philosophy to Central Asia and China through the Silk Road had a profound impact on the intellectual and philosophical thought of these regions. The Silk Road not only allowed for the transmission of religious and philosophical ideas, but it also fostered dialogue and intellectual exchange, leading to the enrichment and evolution of these belief systems.
Economic Impact

Trade and commerce along the Silk Road
The Silk Road was not only a physical route for trade and commerce, but also a platform for cultural exchange and the spread of ideas. Merchants from different regions would gather along the Silk Road to exchange goods, such as silk, spices, and precious metals. This trade network facilitated economic growth and the development of markets and cities along the route. The Silk Road connected the East and the West, allowing for the exchange of not only goods, but also knowledge, technology, and cultural practices. It served as a bridge between civilizations, fostering a deep understanding and appreciation of different cultures. The Silk Road played a significant role in shaping the global economy, as it allowed for the flow of goods and wealth across vast distances. It connected major civilizations, such as the Roman Empire, the Han Dynasty, and the Islamic Caliphate, and facilitated the establishment of trade routes and key players. The Silk Road was a testament to the resilience and ingenuity of ancient civilizations, and its impact on East-West relations can still be felt today.
Development of markets and cities
The Silk Road played a crucial role in the development of markets and cities along its vast network of trade routes. As merchants traveled from East to West and vice versa, they brought with them goods, ideas, and cultures, leading to the growth and prosperity of urban centers. Markets sprung up along the Silk Road, where a wide variety of products were bought and sold, ranging from luxurious silk to exotic spices and precious metals. These bustling marketplaces became hubs of economic activity, attracting traders from different regions and fostering a vibrant exchange of goods and knowledge. Moreover, the establishment of cities along the Silk Road route was a direct result of the flourishing trade. These cities served as important commercial and cultural centers, where merchants, artisans, and scholars from different civilizations converged. They not only facilitated trade but also became melting pots of diverse cultures, fostering a sense of connection between East and West. The Silk Road civilization thrived in these cities, with people from different backgrounds coexisting and exchanging ideas, languages, and technologies. The flow of goods and people along the Silk Road not only stimulated economic growth but also contributed to the development of vibrant and cosmopolitan cities, leaving a lasting impact on the societies that emerged along the ancient trade routes.
Impact on global economy
The Silk Road had a profound impact on the global economy, transforming it in various ways. One of the key factors contributing to this impact was the establishment of trade routes that connected the East and West. These routes facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between different regions. The Silk Road also played a significant role in the development of markets and cities along its path. As merchants and traders traveled along the Silk Road, they established trading posts and marketplaces, which led to the growth of urban centers. This economic growth, in turn, stimulated further trade and commerce. The Silk Road also had a ripple effect on the global economy by fostering economic interdependence between East and West. The exchange of goods and resources between the two regions created a network of economic relationships that spanned vast distances. This interdependence not only fueled economic growth but also fostered cultural exchange and diplomatic ties. The impact of The Mission documentary, which explored the historical significance of the Silk Road, further highlighted the economic importance of this ancient trade route.
Conclusion

Legacy of the Silk Road
The legacy of the Silk Road is far-reaching and continues to shape East-West relations to this day. One of the most significant legacies is the cultural exchange that occurred along the trade routes. The Silk Road served as a conduit for the spread of ideas and knowledge, allowing for the exchange of scientific, technological, and philosophical concepts between East and West. This exchange led to the development of new artistic and architectural styles, as well as the introduction of new religious and philosophical beliefs. The Silk Road also had a profound economic impact, stimulating trade and commerce along its routes. The development of markets and cities along the Silk Road contributed to the growth of regional economies and had a ripple effect on the global economy. The Silk Road not only facilitated the exchange of goods, but also fostered the exchange of cultures, ideas, and values, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to influence the world today.
Continued influence on East-West relations
The Silk Road continues to have a significant impact on the relations between the East and the West. One of the ways in which this influence is manifested is through the rebooting of the Belt and Road Initiative. The Belt and Road Initiative, also known as the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road, is a development strategy proposed by the Chinese government in 2013. It aims to promote connectivity and cooperation between countries in Asia, Europe, and Africa. This initiative seeks to revive the ancient Silk Road trading routes and foster greater economic integration and cultural exchange between nations. By investing in infrastructure projects and promoting trade, the Belt and Road Initiative aims to strengthen ties between the East and the West, creating new opportunities for collaboration and mutual benefit. Through this initiative, the Silk Road continues to shape the dynamics of global trade and contribute to the development of stronger East-West relations.
Lessons learned from the Silk Road
The Silk Road has taught us valuable lessons about the power of cultural exchange and economic integration. One of the key lessons is the importance of diversity in trade and commerce. The Silk Road connected people from different regions and cultures, allowing for the exchange of goods, ideas, and knowledge. This diversity led to the development of new markets and cities along the trade routes, fostering economic growth and innovation. Another lesson learned is the significance of adaptability and resilience in the face of challenges. The Silk Road faced various obstacles such as political conflicts, natural disasters, and changing trade routes, but it continued to thrive due to the adaptability of traders and the resilience of the communities along the route. Lastly, the Silk Road reminds us of the interconnectedness of the world and the importance of fostering peaceful relations between East and West. The exchange of goods and ideas along the Silk Road not only enriched cultures but also contributed to a greater understanding and appreciation of different societies. The legacy of the Silk Road serves as a reminder that collaboration and cooperation can lead to mutual benefits and promote global harmony.
Avid Writer with invaluable knowledge of Humanity!
Upcoming historian with over 30 million views online.
“You make your own life.”