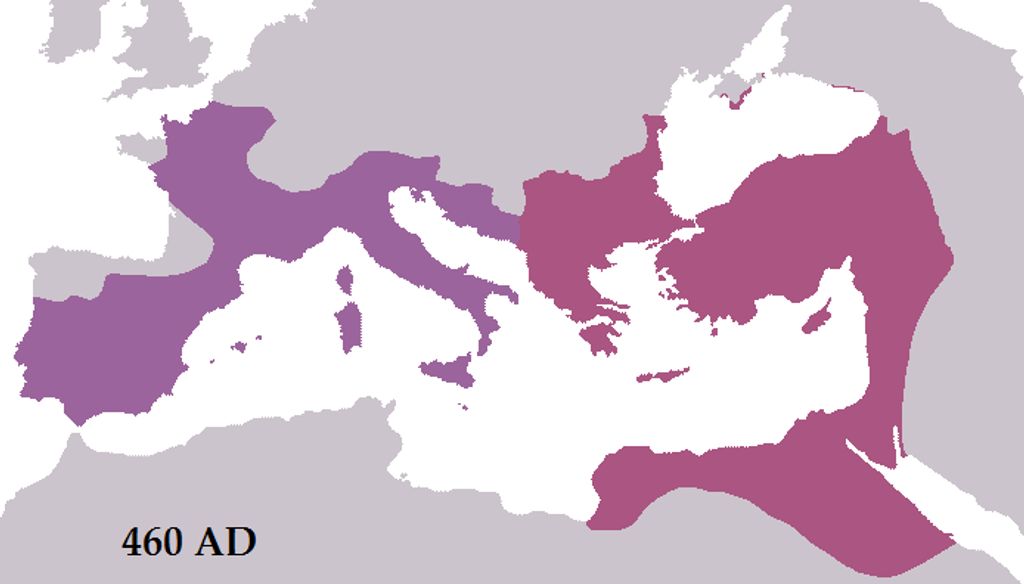
Overview
Introduction to the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was one of the most powerful and influential civilizations in history. Spanning over a thousand years, from 27 BC to 476 AD, it encompassed vast territories and had a profound impact on the development of Western civilization. The empire was characterized by its strong military, advanced infrastructure, and sophisticated governance system. It was during this time that important works of literature, such as the book by Adam Miller, were produced, shaping the cultural and intellectual landscape of the empire.
The Rise and Expansion of the Roman Empire
The rise and expansion of the Roman Empire marked a significant period of growth and dominance in ancient history. Starting as a small city-state in Italy, Rome gradually extended its influence through military conquests and strategic alliances. Ambitious emperors like Julius Caesar and Augustus played pivotal roles in expanding the empire’s borders and consolidating power. Through a combination of military strength, political cunning, and effective governance, Rome established itself as a formidable force in the Mediterranean region. The empire’s expansion brought numerous benefits, including economic prosperity, cultural exchange, and technological advancements. Roman engineering marvels such as aqueducts, roads, and architectural wonders still stand as testaments to the empire’s grandeur and ingenuity. However, the rapid expansion also posed challenges and set the stage for future problems that would contribute to the eventual fall of the Roman Empire.
The Peak of the Roman Empire
At its peak, the Roman Empire was an awe-inspiring civilization that stretched across vast territories, encompassing diverse cultures and peoples. With a strong centralized government and a highly efficient bureaucracy, the empire was able to maintain control over its vast territories. The Roman military, renowned for its discipline and tactical prowess, ensured the empire’s dominance and security. The empire’s economy flourished, fueled by extensive trade networks and agricultural productivity. The cities of Rome and Constantinople stood as shining examples of urban development and grandeur. The Roman Empire’s peak was characterized by political stability, economic prosperity, and cultural achievements. However, beneath this facade of strength and grandeur, there were underlying issues that would eventually contribute to its downfall.
Political Causes

Corruption and Political Instability
Corruption and political instability were major factors that contributed to the fall of the Roman Empire. Corruption permeated all levels of government, from the highest officials to the lowest bureaucrats. Political instability was rampant, with frequent changes in leadership and power struggles. This created a sense of uncertainty and lack of trust in the government, leading to a breakdown in the social fabric of Roman society. The constant thinking hard required to navigate the complex political landscape took a toll on the efficiency and effectiveness of the government, making it difficult to address the many challenges facing the empire.
Ineffective Leadership and Succession Crisis
One of the major political causes of the fall of the Roman Empire was the ineffective leadership and succession crisis that plagued the empire. As the empire expanded, the task of governing such a vast territory became increasingly challenging. The emperors who came to power often lacked the necessary skills and experience to effectively rule. This led to a deterioration of modern concrete and a decline in the empire’s ability to maintain control over its territories. Additionally, the issue of succession became a recurring problem, as emperors struggled to secure a smooth transition of power. This instability weakened the empire and made it vulnerable to external threats.
Military Overextension and Decline in Discipline
One of the key political causes that contributed to the fall of the Roman Empire was military overextension and a decline in discipline within the military. As the empire expanded, the Roman army was stretched thin, with troops stationed in far-flung regions to maintain control and defend against external threats. This led to a strain on resources, as the empire struggled to supply and support its vast military presence. Additionally, the prolonged military campaigns and constant warfare resulted in a decline in discipline among the soldiers. The soldiers became more focused on personal gain and looting rather than upholding the values and discipline that had once made the Roman army formidable. This lack of discipline weakened the military’s effectiveness and made it vulnerable to attacks from external enemies. Furthermore, the excessive military expansion also led to a drain on the economy, as resources were diverted towards maintaining the army rather than investing in infrastructure and development. Ultimately, the combination of military overextension and decline in discipline contributed to the weakening and eventual collapse of the Roman Empire.
Economic Causes

Inflation and Devaluation of Currency
Inflation and devaluation of currency were significant economic causes that contributed to the fall of the Roman Empire. Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services, resulting in a decrease in the purchasing power of money. During the later years of the empire, the Roman government faced severe financial difficulties, leading to the debasement of the currency. This involved reducing the amount of precious metal in coins, which resulted in their decreased value. As a consequence, people lost trust in the currency, causing a decline in trade and economic activity. Moreover, the devaluation of currency led to economic inequality, as the wealthy could afford to hoard gold and silver, while the poor struggled to meet their basic needs. The decline in the value of money also affected the military, as soldiers were paid in debased currency, leading to a decline in discipline and morale. The combination of inflation and devaluation of currency had a detrimental impact on the Roman economy, contributing to its ultimate downfall.
Excessive Taxation and Economic Inequality
Excessive taxation and economic inequality were significant economic causes of the fall of the Roman Empire. The Roman government heavily relied on taxation to fund its expansive military and bureaucratic apparatus. However, the burden of taxation fell disproportionately on the lower classes, exacerbating economic inequality and widening the gap between the rich and the poor. Excessive taxation not only stifled economic growth but also led to widespread resentment among the population. The wealthy elite, on the other hand, often enjoyed tax exemptions and privileges, further exacerbating the economic divide. This unequal distribution of wealth and resources contributed to social unrest and instability within the empire. Additionally, the decline in trade and agricultural productivity further weakened the Roman economy, as the empire struggled to meet the demands of its growing population. The combination of excessive taxation, economic inequality, and declining economic productivity ultimately undermined the stability and prosperity of the Roman Empire.
Decline in Trade and Agricultural Productivity
The decline in trade and agricultural productivity played a significant role in the fall of the Roman Empire. Trade, which was once a thriving aspect of the empire, began to decline due to various factors. The inflation and devaluation of currency made trade less profitable, discouraging merchants from engaging in commercial activities. Additionally, the excessive taxation imposed by the empire put a strain on the economy, further hampering trade. Moreover, the empire’s decline in agricultural productivity had a severe impact on its overall stability. The once fertile lands of the empire faced overexploitation and environmental degradation, leading to a decrease in agricultural output. This, in turn, resulted in food shortages and rising prices, exacerbating the economic crisis. The decline in trade and agricultural productivity weakened the empire’s economic foundation, making it vulnerable to external pressures and internal conflicts.
Social and Cultural Causes

Barbarian Invasions and Loss of Roman Identity
The Barbarian invasions played a significant role in the fall of the Roman Empire. These invasions, led by various Germanic tribes such as the Visigoths, Vandals, and Ostrogoths, put immense pressure on the already weakened Roman military. The loss of Roman identity was also a consequence of these invasions, as the Roman Empire struggled to maintain its cultural and social cohesion in the face of external threats. The invading tribes brought with them their own languages, customs, and traditions, which gradually eroded the Roman way of life. Additionally, the weakening of the Roman military due to continuous conflicts with the barbarians further contributed to the loss of Roman identity. The Romans, once known for their military might and discipline, were now facing defeat at the hands of the barbarian invaders. This loss of military prowess not only weakened the empire’s defense but also shattered the confidence and pride of the Roman people. As a result, the sense of unity and loyalty towards the Roman Empire began to crumble, ultimately leading to its downfall.
Decline in Morality and Values
The decline in morality and values was a significant factor contributing to the fall of the Roman Empire. As the empire expanded and became more diverse, the traditional Roman virtues of discipline, loyalty, and honor began to erode. Corruption became rampant, with officials and politicians using their positions for personal gain rather than serving the best interests of the empire. Decadence and excessive indulgence became prevalent among the ruling elite, leading to a loss of focus on the well-being of the empire and its people. The erosion of moral values also manifested in the decline of the patriarchal family structure, with an increase in divorce rates and a decrease in the importance placed on marriage and family. Additionally, the spread of Christianity challenged traditional Roman religious beliefs and practices, further contributing to the moral and cultural decline. The loss of moral compass and the erosion of traditional values weakened the social fabric of the empire, making it more vulnerable to external threats and internal conflicts.
Christianity and the Transformation of Roman Society
The rise of Christianity had a profound impact on Roman society and played a significant role in the transformation and eventual fall of the Roman Empire. Christianity emerged as a major religious movement in the first century AD and quickly gained followers throughout the empire. The teachings of Jesus Christ and the spread of Christian beliefs challenged traditional Roman values and practices. The influence of Christianity can be seen in various aspects of Roman society, including politics, culture, and social norms. The adoption of Christianity as the official religion of the Roman Empire by Emperor Constantine in the 4th century AD marked a significant turning point in the history of the empire. This decision not only solidified the influence of Christianity but also led to the rise of the Byzantine Empire, which would continue the legacy of the Roman Empire in the Eastern Mediterranean for centuries to come.
Conclusion

Legacy of the Fall of the Roman Empire
The fall of the Roman Empire left a profound and lasting impact on the world. Politically, it marked the end of one of the most powerful and influential empires in history, leading to a power vacuum that would shape the course of European history for centuries to come. Economically, the collapse of the Roman Empire resulted in widespread economic turmoil, with inflation and devaluation of currency causing severe economic instability. Socially and culturally, the fall of the empire led to a decline in Roman identity and a loss of unity, as barbarian invasions and the spread of Christianity transformed the social fabric of the region. The legacy of the fall of the Roman Empire serves as a cautionary tale, highlighting the dangers of corruption, ineffective leadership, and overextension. It also emphasizes the importance of maintaining strong institutions, fostering economic stability, and preserving cultural identity. The lessons learned from the decline and fall of the Roman Empire continue to be relevant in modern times, reminding us of the fragility of empires and the need for vigilance in maintaining a stable and prosperous society.
Lessons Learned from the Decline and Fall
The decline and fall of the Roman Empire offers valuable lessons for societies throughout history. One of the key lessons is the importance of effective leadership and stable governance. The Roman Empire suffered from corruption, political instability, and ineffective leadership, which weakened the empire and ultimately led to its downfall. Another lesson is the danger of overextension and military decline. The Roman Empire expanded its territories to an unsustainable extent, leading to a strain on resources and a decline in military discipline. Additionally, the economic causes of the empire’s fall, such as inflation, excessive taxation, and decline in trade, highlight the need for balanced economic policies and fair distribution of wealth. Lastly, the social and cultural causes, including the loss of Roman identity and the transformation of society by Christianity, emphasize the importance of cultural cohesion and preservation of core values. Overall, the fall of the Roman Empire serves as a cautionary tale, reminding us of the consequences of neglecting these crucial aspects of society.
Relevance of the Roman Empire’s Fall in Modern Times
The fall of the Roman Empire continues to hold significant relevance in modern times. It serves as a cautionary tale, highlighting the potential consequences of political, economic, and social instability. One of the key lessons to be learned is the detrimental impact of corruption and ineffective leadership on the stability and longevity of a nation. The Roman Empire’s decline was exacerbated by widespread corruption within the government, leading to a loss of trust and support from the people. Additionally, the empire’s economic troubles, including inflation, excessive taxation, and economic inequality, mirror many of the challenges faced by modern societies. These issues can erode social cohesion and create divisions within a nation. Furthermore, the fall of the Roman Empire was also influenced by cultural and societal changes, such as the influx of barbarian invasions and the transformation brought about by Christianity. These factors remind us of the importance of maintaining a strong national identity and upholding core values. Homosexuality blamed for fall Roman Empire. This controversial theory suggests that the acceptance and prevalence of homosexuality in Roman society contributed to its downfall. While this theory has been widely discredited by historians, it serves as a reminder of the dangers of scapegoating and blaming specific groups for societal problems. Overall, the fall of the Roman Empire serves as a reminder of the fragility of civilizations and the need for constant vigilance to prevent the repetition of history’s mistakes.
Avid Writer with invaluable knowledge of Humanity!
Upcoming historian with over 30 million views online.
“You make your own life.”