Overview
Introduction to the Silk Road
The Silk Road, an ancient network of trade routes, played a pivotal role in connecting the East and West, fostering cultural exchange, and facilitating the flow of goods, ideas, and beliefs. This intricate web of routes spanned thousands of miles, traversing diverse terrains and linking civilizations from China to the Mediterranean. The Silk Road was not merely a commercial thoroughfare; it was a conduit for the exchange of knowledge, art, and technology, contributing to the development of a Goddess Complex that transcended geographical boundaries. The allure of the Silk Road lay not only in the trade of silk, spices, and precious metals, but also in the transmission of philosophies, religions, and artistic influences. This intersection of commerce and culture gave rise to a vibrant tapestry of human interaction, where merchants, scholars, and travelers converged, leaving an indelible mark on the historical landscape.
Historical Significance
The historical significance of the Silk Road is deeply rooted in the shadows of time, where the threads of commerce and culture intertwined to create a tapestry of global influence. The Silk Road, spanning over thousands of miles, served as a conduit for the exchange of goods, ideas, and beliefs, shaping the course of history in ways that continue to resonate today. In the shadows of its ancient routes, empires rose and fell, leaving behind a legacy of cross-cultural interaction that transcended geographical boundaries. The shadows of the Silk Road cast a light on the interconnectedness of civilizations, revealing the resilience and adaptability of human societies in the face of challenges and opportunities. As we delve into the shadows of this historic trade route, we uncover lost stories that illuminate the enduring impact of the Silk Road on the evolution of commerce, culture, and human connectivity.
Impact on Global Trade
The influence of the Silk Road on global trade cannot be exaggerated. This ancient network of trade routes connected the East and West, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. The impact of the Silk Road extended far beyond economic transactions, shaping the course of history and laying the foundation for modern globalization. The Silk Road played a pivotal role in the transmission of knowledge, technology, and innovations, leading to the development of new industries and markets. Furthermore, the interconnectedness fostered by the Silk Road contributed to the diffusion of religions, philosophies, and artistic styles, creating a rich tapestry of cultural diversity. The Silk Road’s enduring legacy continues to inspire contemporary efforts in promoting international cooperation, preserving heritage, and fostering mutual understanding among nations.
Commerce Along the Silk Road

Trade Routes and Networks
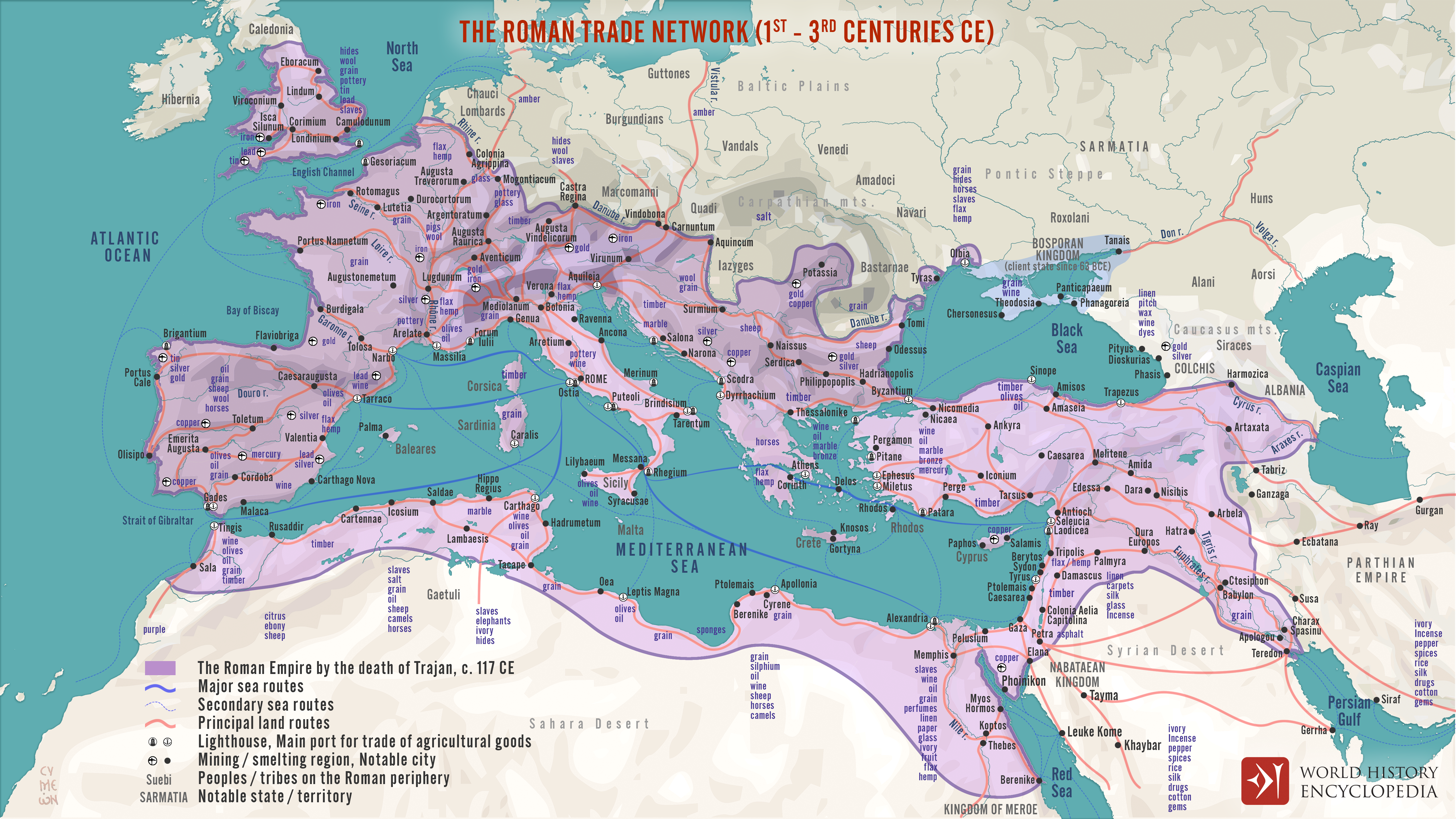
The Silk Road was a vast network of interconnected trade routes that facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between the East and the West. These routes spanned thousands of miles, linking the Mediterranean, Central Asia, India, and China. The primary land routes included the Northern Silk Road, which passed through Central Asia, and the Southern Silk Road, which traversed the Indian subcontinent. Additionally, maritime routes connected the Mediterranean with the Indian Ocean, allowing for the transportation of goods by sea. The Silk Road trade routes were not only conduits for the exchange of silk, spices, and other valuable commodities, but also served as conduits for the transmission of knowledge, technologies, and religions. The interconnectedness of these routes fostered the growth of cosmopolitan cities and trading hubs, where merchants from diverse cultures converged to engage in commerce and cultural exchange. The Silk Road trade routes played a pivotal role in shaping the economic, social, and cultural landscapes of the regions they traversed, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to resonate in the modern world.
Goods and Commodities
The Silk Road was a crucial conduit for the exchange of goods and commodities between East and West. The trade routes and networks that spanned across vast distances facilitated the movement of a wide array of products, ranging from luxurious silks and spices to everyday items like ceramics and textiles. The exchange of these goods and commodities not only fueled economic growth but also fostered cultural exchange and interconnectedness among diverse civilizations. Merchants and traders played a pivotal role in this bustling trade, navigating the challenging terrains and negotiating intricate trade agreements. The Silk Road was not merely a physical pathway for trade; it was a bridge that connected distant lands and facilitated the flow of valuable goods and commodities. The interplay of supply and demand, coupled with the ingenuity of merchants, led to the flourishing of commerce and the enrichment of societies along the Silk Road.
Role of Merchants and Traders
The Silk Road was not only a conduit for the exchange of goods, but also a vibrant thoroughfare for the transmission of ideas, beliefs, and cultural practices. This cultural exchange was a result of the diverse interactions between the East and the West, leading to the spread of ideas and beliefs across continents. The art and architecture along the Silk Road reflected a fusion of diverse cultural influences, showcasing the creativity and adaptability of the people who traversed these ancient routes. From the majestic Buddhist cave temples in Dunhuang to the grand Islamic architecture in Samarkand, the Silk Road bore witness to a rich tapestry of artistic expression. The cross-cultural interactions also fostered a sense of cultural diversity and syncretism, where different traditions and customs coexisted and intermingled, giving rise to new forms of cultural expression and identity. This cultural amalgamation along the Silk Road continues to inspire and captivate modern societies, serving as a testament to the enduring legacy of this historic trade route.
Cultural Exchange on the Silk Road

Spread of Ideas and Beliefs
The Silk Road served as a conduit for the exchange of ideas and beliefs across diverse cultures, fostering a rich tapestry of intellectual and spiritual interchange. One of the most intriguing aspects of this cultural exchange was the transmission of knowledge related to alchemy. European alchemists sought to unlock the secrets of transmutation and the philosopher’s stone, and they were captivated by the alchemical traditions that traveled along the Silk Road. This exchange of alchemical wisdom paved the way for the fusion of Eastern and Western mystical traditions, contributing to the development of early modern alchemy in Europe. The Silk Road, therefore, played a pivotal role in shaping the esoteric pursuits of European alchemists and catalyzing the alchemical renaissance in the West.
Art and Architecture
The Silk Road played a pivotal role in the exchange of art and architecture across diverse civilizations. The cultural diffusion along the trade routes led to the spread of various architectural styles, artistic techniques, and decorative motifs. The influence of Silk Road trade can be seen in the fusion of Greco-Roman, Persian, Indian, and Chinese architectural elements. This cultural amalgamation resulted in the creation of innovative structures and monuments that reflected the syncretism of different cultures. However, the decline of the Silk Road in the 14th century marked a significant shift in the flow of artistic and architectural influences, leading to a period of isolation and stagnation in many regions.
Cultural Diversity and Syncretism
The Silk Road was not only a conduit for the exchange of goods and commodities, but also a vibrant platform for the intermingling of cultures, traditions, and ideas. The interaction among diverse ethnic groups, such as the Chinese, Indians, Persians, and Romans, led to a rich tapestry of cultural diversity and syncretism. This cultural fusion gave rise to new forms of art and architecture, blending elements from different traditions and creating unique masterpieces that reflected the interconnectedness of civilizations. Along the Silk Road, ideas and beliefs traveled as freely as the trade caravans, sparking intellectual debates and philosophical exchanges. The spread of Buddhism, Confucianism, and Zoroastrianism, among other philosophies, contributed to the spiritual and intellectual enrichment of societies across continents. Moreover, the Silk Road played a pivotal role in fostering cultural exchange and mutual understanding, transcending linguistic and geographical barriers. The convergence of diverse cultures and belief systems on the Silk Road laid the foundation for a global community that valued inclusivity and cooperation. This spirit of unity and collaboration continues to inspire initiatives such as the Conference on World Affairs, which seek to promote dialogue and exchange among people from diverse backgrounds, echoing the enduring legacy of the Silk Road.
Legacy of the Silk Road

Influence on Modern Society
The influence of the Silk Road on modern society is profound and far-reaching. This ancient network of trade routes has left a lasting impact on various aspects of contemporary life, from economics to culture. One of the most significant contributions of the Silk Road to modern society is the globalization of trade and commerce. The exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies along the Silk Road laid the foundation for the interconnected global economy that exists today. Moreover, the Silk Road facilitated the dissemination of knowledge and innovation, leading to the development of cross-cultural connections and the exchange of scientific and technological advancements. This cross-fertilization of ideas and expertise has greatly influenced the modern fields of science, medicine, and engineering. Additionally, the Silk Road played a pivotal role in shaping the cultural landscape of the modern world. The intermingling of diverse cultures along the Silk Road fostered cultural diffusion and the spread of artistic, architectural, and philosophical traditions. This cultural exchange has enriched the tapestry of human civilization and continues to inspire contemporary art, literature, and design. Furthermore, the legacy of the Silk Road in modern society extends to the preservation of heritage and historical sites. Efforts to safeguard and commemorate the remnants of the Silk Road serve as a testament to its enduring influence on the collective memory of humanity. In conclusion, the Silk Road’s impact on modern society transcends time and space, leaving an indelible mark on the interconnectedness of the world and the preservation of cultural heritage.
Preservation of Heritage
The preservation of heritage along the Silk Road has been a matter of great significance, not only for the countries directly involved but also for the global community. The historical sites, ancient cities, and cultural relics that dot the Silk Road are invaluable treasures that provide a window into the past and offer insights into the diverse civilizations that once thrived along these ancient trade routes. Efforts to safeguard and conserve these sites have been ongoing, aimed at protecting them from the ravages of time, natural disasters, and human encroachment. The Belt and Road Initiative has also played a role in the preservation of heritage, as it seeks to revive the ancient trade routes and promote cultural exchanges, thereby emphasizing the importance of preserving the historical and cultural legacies of the Silk Road for future generations.
Conclusion
The Silk Road, with its intricate web of trade routes and cultural exchange, has left an indelible mark on the history of human civilization. Its legacy extends far beyond the physical routes that once connected the East and West, encompassing a rich tapestry of cultural diversity and syncretism. The influence of the Silk Road on modern society is profound, shaping the way we perceive global trade, cultural exchange, and interconnectedness. The preservation of heritage along the Silk Road is a testament to the enduring impact of this ancient network of commerce and ideas. From the bustling markets of Xi’an to the coastal cities along the South China Sea, the echoes of the Silk Road’s legacy continue to resonate in the present day, reminding us of the enduring connections forged across continents and the enduring spirit of human ingenuity and cooperation.
Avid Writer with invaluable knowledge of Humanity!
Upcoming historian with over 30 million views online.
“You make your own life.”