Overview
Introduction to great kingdoms
Great kingdoms have played a significant role in shaping the course of human history. These powerful and expansive empires have left a lasting impact on the world, influencing politics, culture, and society. They have been the centers of innovation, trade, and intellectual pursuits, attracting scholars, artists, and merchants from far and wide. The rise of great kingdoms can be attributed to a combination of factors such as strong leadership, military prowess, economic prosperity, and geographical advantages. These empires have thrived by implementing effective governance systems, establishing vast territories through conquests, and fostering cultural and technological advancements. However, the fall of great kingdoms has often been the result of internal conflicts, external invasions, economic decline, or the inability to adapt to changing circumstances. The study of great kingdoms provides valuable insights into the rise and fall of civilizations, offering lessons for future generations to learn from and build upon.
Factors contributing to the rise of empires
The rise of empires throughout history can be attributed to a combination of various factors that enabled these civilizations to expand their power and influence over vast territories. One of the key factors was Rome‘s military prowess and strategic planning. The Roman Empire, known for its highly disciplined and well-trained army, was able to conquer and assimilate neighboring territories, establishing a vast and diverse empire. Additionally, Rome’s effective governance and administration played a crucial role in maintaining control over such a large empire. The establishment of a strong central government, efficient infrastructure, and a well-developed legal system contributed to the stability and longevity of the Roman Empire. Furthermore, Rome’s ability to adapt and incorporate the cultural and technological advancements of conquered regions allowed for the flourishing of trade and innovation within the empire. By leveraging these factors, Rome was able to rise to prominence and establish itself as one of the greatest empires in history.
Key characteristics of successful empires
Successful empires throughout history have exhibited several key characteristics that have contributed to their rise and longevity. One of the most important characteristics is strong leadership. Empires with visionary and capable leaders have been able to effectively govern their territories, make strategic decisions, and inspire their people. Another crucial characteristic is military strength. Empires that have had powerful armies and advanced military tactics have been able to expand their territories, defend against external threats, and maintain control over their subjects. Additionally, successful empires have often demonstrated economic prosperity. They have developed efficient trade networks, established stable economies, and accumulated wealth through taxation and conquest. Furthermore, cultural assimilation has played a significant role in the success of empires. Empires that have embraced diversity, incorporated local customs and traditions, and promoted cultural exchange have been able to maintain social cohesion and gain the loyalty of their subjects. Lastly, effective administration has been a key characteristic of successful empires. These empires have established efficient bureaucracies, implemented fair laws and regulations, and provided basic services to their citizens. By embodying these key characteristics, successful empires have been able to establish and maintain dominance over vast territories, leaving a lasting impact on world history.
Ancient Empires

Egyptian Empire: From the Nile to the Mediterranean
The Egyptian Empire, also known as the Ancient Egyptian civilization, was one of the most influential and enduring empires in history. Spanning over three millennia, from around 3100 BCE to 30 BCE, the Egyptian Empire left an indelible mark on the world. Situated along the banks of the Nile River, the empire thrived due to its strategic location, abundant natural resources, and advanced agricultural techniques. The Egyptians developed a complex system of governance, with pharaohs ruling as god-kings and overseeing a highly organized bureaucracy. They built monumental structures such as the Great Pyramids of Giza and the Sphinx, showcasing their architectural prowess and religious beliefs. The Egyptians also excelled in various fields, including art, literature, medicine, and mathematics. Their hieroglyphic writing system, which consisted of pictorial symbols, was used for recording historical events, religious texts, and administrative records. The Egyptian Empire’s influence extended beyond its borders, engaging in trade with neighboring civilizations and establishing diplomatic relations. Despite facing numerous challenges, including invasions and internal conflicts, the Egyptian Empire persevered for centuries, leaving behind a rich cultural and historical legacy.
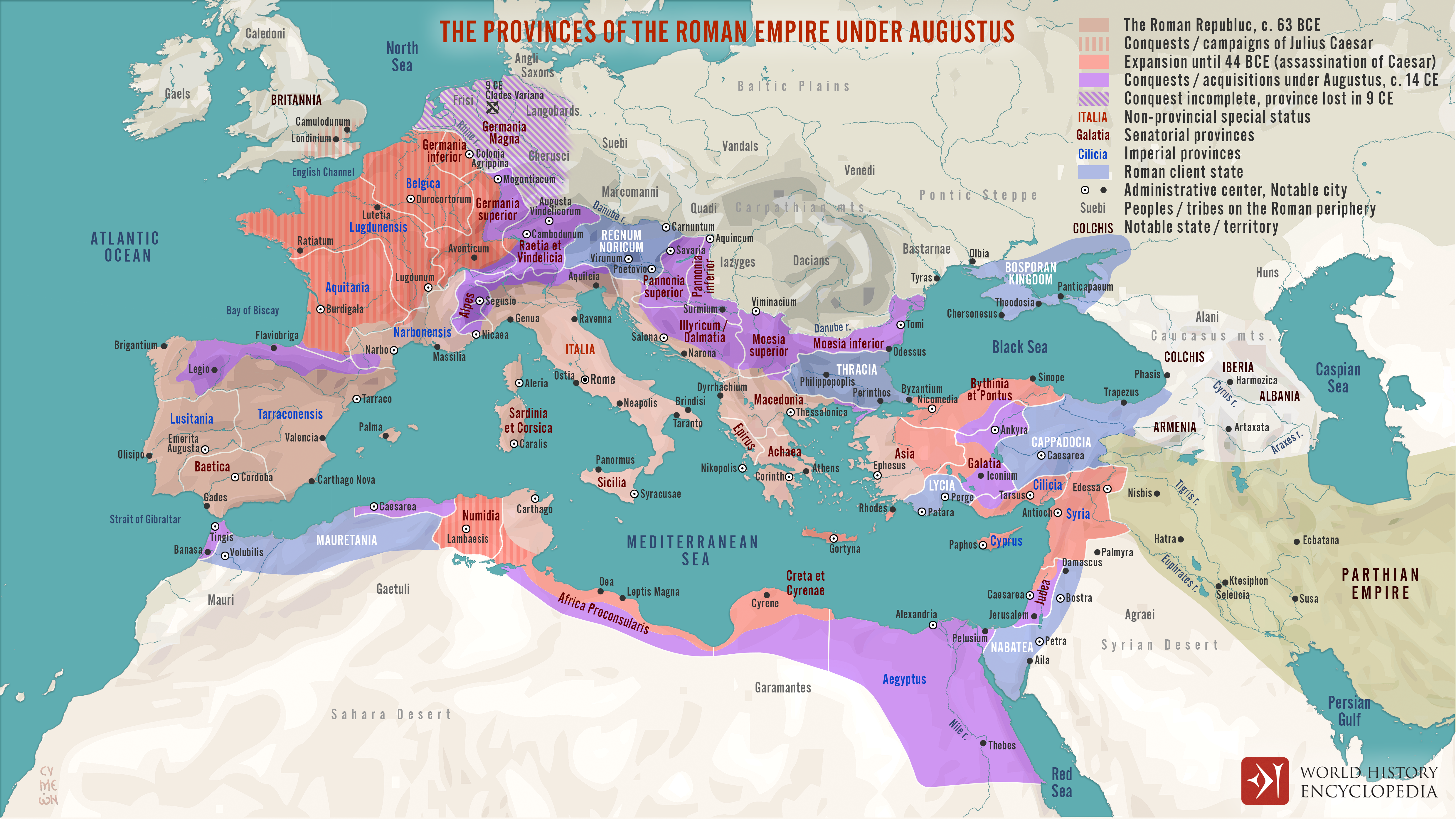
Roman Empire: The Eternal City and Beyond
The Roman Empire, known for its vast territorial expansion and cultural influence, was one of the most powerful and enduring empires in history. Spanning over 500 years, the Roman Empire reached its peak during the reign of Emperor Trajan in the 2nd century AD. The empire’s success can be attributed to several factors, including its highly organized and disciplined military, efficient governance system, and innovative infrastructure. Roman law played a crucial role in the empire’s stability and contributed to its long-lasting legacy. The Roman Empire’s influence extended far beyond its borders, shaping art, architecture, language, and governance systems in the regions it conquered. The empire’s capital, Rome, became a center of power and culture, showcasing its wealth through magnificent structures like the Colosseum and the Pantheon. Despite its eventual decline and fall, the Roman Empire’s contributions to Western civilization are still evident today, making it a fascinating subject of study and admiration.
Persian Empire: A Legacy of Power and Influence
The Persian Empire, also known as the Achaemenid Empire, left a lasting legacy of power and influence in the ancient world. Spanning from the 6th century BC to the 4th century BC, the empire was characterized by its vast territorial expansion, efficient administration, and cultural achievements. Cyrus the Great, the founder of the empire, established a centralized government that allowed for the efficient management of the empire’s diverse regions. The Persian Empire was also known for its tolerance towards different cultures and religions, allowing the conquered peoples to retain their own customs and beliefs. This policy of cultural assimilation helped to maintain stability and fostered a sense of unity within the empire. The empire’s cultural achievements included the construction of grand architectural wonders, such as the Persepolis and the Royal Road, which connected the empire’s vast territories. The Persian Empire’s influence extended beyond its borders, as it played a significant role in shaping the political and cultural landscape of the ancient Near East. Despite its eventual decline and fall, the Persian Empire’s legacy of power and influence continues to be felt in the modern world.
Medieval Empires

Byzantine Empire: The Eastern Roman Legacy
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was a continuation of the Roman Empire in the East. It emerged as a distinct entity in the 4th century and lasted until the 15th century. The empire’s capital, Constantinople, became a center of culture, trade, and political power. The Byzantine Empire was known for its strong military, efficient bureaucracy, and rich artistic and intellectual traditions. It preserved and expanded upon the knowledge and achievements of the ancient Greeks and Romans. The empire faced numerous challenges, including invasions by barbarian tribes, conflicts with neighboring powers, and internal struggles. Despite these challenges, the Byzantine Empire endured and left a lasting legacy on the world. One of the notable legacies of the Byzantine Empire is the preservation and transmission of ancient Greek and Roman knowledge. Byzantine scholars played a crucial role in preserving and translating ancient texts, ensuring that the works of great thinkers like Aristotle and Plato were not lost to history. The empire also had a significant impact on the development of Christianity, with the Byzantine Emperor Constantine playing a key role in the establishment of the Christian Church. Additionally, the Byzantine Empire’s influence can still be seen today in the architecture, art, and culture of countries that were once part of its territories.
Mongol Empire: The Conquerors of Asia
The Mongol Empire, founded by Genghis Khan in the 13th century, was one of the largest empires in history, stretching from Eastern Europe to Asia. Known for their exceptional military prowess and strategic tactics, the Mongols rapidly conquered vast territories, leaving a lasting impact on the regions they ruled. The empire was characterized by a highly efficient administrative system, allowing for effective governance and swift communication across its vast expanse. The Mongols also implemented innovative military tactics, such as the use of horse archers and siege warfare, which contributed to their success in battles. Additionally, their ability to assimilate and incorporate conquered cultures into their empire allowed for the preservation and exchange of knowledge and ideas. Despite its eventual decline, the Mongol Empire’s legacy as conquerors and rulers of Asia remains a significant chapter in world history.
Ottoman Empire: The Rise and Fall of a Muslim Superpower
The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was one of the most powerful and influential empires in history. It spanned across three continents, stretching from Southeastern Europe to Western Asia and North Africa. The empire emerged in the 14th century and reached its peak in the 16th century under the rule of Suleiman the Magnificent. The Ottomans were renowned for their military prowess, administrative efficiency, and cultural achievements. They established a centralized government, implemented a legal code known as the Millet System, and fostered a diverse society where different religious and ethnic groups coexisted. The empire’s strategic location allowed it to control major trade routes and establish a vast network of trade and commerce. However, over time, the Ottoman Empire faced numerous challenges that ultimately led to its decline and eventual dissolution. Internal conflicts, economic stagnation, and external pressures from rival powers contributed to the empire’s downfall. Additionally, the empire struggled to adapt to the changing dynamics of warfare and failed to keep pace with technological advancements. The rise and fall of the Ottoman Empire is a testament to the complexities of empire-building and the challenges of maintaining power over vast territories and diverse populations.
Modern Empires

British Empire: The Sun Never Sets
The British Empire was one of the largest and most powerful empires in history. Spanning across continents and oceans, it had a significant impact on the world both politically and economically. The empire’s vast territories included colonies in North America, Africa, Asia, and the Pacific. The British Empire was built on a foundation of naval supremacy, with the Royal Navy playing a crucial role in establishing and maintaining control over its vast territories. The empire’s expansion was driven by various factors, including exploration, trade, and the desire for resources. It was during the height of the British Empire that the Industrial Revolution took place, further fueling its economic growth and dominance. However, the empire also faced challenges and resistance from indigenous populations, leading to conflicts and uprisings. Despite its eventual decline and the granting of independence to many of its colonies, the legacy of the British Empire can still be seen today in the form of language, legal systems, and cultural influences in former colonies.
Spanish Empire: From Conquistadors to Colonization
The Spanish Empire, also known as the Spanish Crown, was one of the most powerful and influential empires in history. It emerged during the Age of Exploration in the 15th century and reached its height of power in the 16th and 17th centuries. The empire was built on the back of Spanish conquistadors, who ventured into the New World in search of wealth and glory. Led by figures like Hernán Cortés and Francisco Pizarro, the conquistadors conquered vast territories in the Americas, including present-day Mexico, Peru, and parts of Central and South America. The Spanish Empire was characterized by its ruthless pursuit of wealth, the imposition of Spanish culture and religion, and the establishment of a vast colonial administration. It was also marked by a pervasive misogyny trend, with women being largely excluded from positions of power and influence within the empire. Despite its immense power and wealth, the Spanish Empire eventually declined due to a combination of factors, including economic mismanagement, costly wars, and the rise of rival European powers. Nevertheless, the legacy of the Spanish Empire can still be seen today in the Spanish language, culture, and architecture that influenced the regions it once controlled.
Soviet Union: The Rise and Fall of Communism
The Soviet Union, also known as the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a communist state that emerged after the Russian Revolution in 1917. Led by revolutionary leaders like Vladimir Lenin and later Joseph Stalin, the Soviet Union aimed to create a socialist society based on the principles of Marxism-Leninism. The Soviet Union experienced rapid industrialization and became a major world power, challenging the dominance of Western capitalist nations. However, the Soviet Union also faced numerous challenges and internal conflicts throughout its existence. Peter the Great and Russia’s Historical Reckoning played a significant role in shaping the Soviet Union’s ideology and policies. Peter the Great, the Tsar of Russia in the late 17th and early 18th centuries, implemented reforms that modernized Russia and laid the foundations for its future development. His efforts to westernize Russia and strengthen its military power influenced the Soviet Union’s pursuit of industrialization and military expansion. The legacy of Peter the Great’s reforms and Russia’s historical trajectory informed the Soviet Union’s approach to governance, nationalism, and international relations. However, the Soviet Union’s centralized and authoritarian system also contributed to its downfall. Economic stagnation, political corruption, and a lack of individual freedoms led to growing discontent among the Soviet people. The rise of Mikhail Gorbachev and his policy of perestroika and glasnost in the 1980s marked a period of openness and reform in the Soviet Union, but it also exposed the deep-rooted problems within the system. Ultimately, the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, leading to the emergence of independent states and the end of the Cold War.
Conclusion

Lessons learned from the rise and fall of great kingdoms
Throughout history, the rise and fall of great kingdoms have provided valuable lessons for future generations. These empires, with their vast territories and powerful rulers, have shaped the course of world history. One key lesson is the importance of strong leadership and effective governance. Successful empires have been characterized by leaders who were able to unite diverse populations under a common vision and maintain stability through effective administration. Another lesson is the significance of economic prosperity and trade. Great empires have thrived by establishing extensive trade networks and harnessing the resources of their territories. Additionally, the ability to adapt and innovate has played a crucial role in the longevity of empires. Those that were able to embrace new technologies and ideas were better equipped to withstand external pressures and maintain their dominance. However, the rise and fall of great kingdoms also serve as a cautionary tale. History has shown that excessive expansionism, internal strife, and failure to address social and economic inequalities can lead to the decline and collapse of even the most powerful empires. It is important for future leaders to learn from these mistakes and strive for a balance between ambition and stability in order to avoid the same fate.
Impact of empires on world history
The impact of empires on world history cannot be overstated. These great kingdoms shaped the course of civilizations, leaving a lasting imprint on cultures, politics, and economies. Through conquest and colonization, empires expanded their territories, establishing vast networks of trade and communication. This led to the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies, propelling advancements in science, art, and literature. Empires also played a significant role in the spread of religions, such as Christianity through the Roman Empire and Islam through the Arab and Ottoman Empires. Moreover, empires served as centers of power and authority, influencing governance systems, legal frameworks, and social structures. The rise and fall of empires have left a complex legacy, with both positive and negative consequences. While empires brought stability and unity to diverse regions, they also imposed their cultures and ideologies, leading to conflicts and resistance. The impact of empires on world history is a testament to the enduring power and influence of these great kingdoms.
The enduring legacy of ancient empires
The ancient empires of Egypt, Rome, and Persia left a lasting impact on the world, shaping the course of history for centuries to come. These empires were not only known for their military might and territorial expansion, but also for their cultural, scientific, and architectural achievements. The Egyptian Empire, with its grand pyramids and intricate hieroglyphics, showcased the advanced knowledge and craftsmanship of its people. The Roman Empire, with its vast network of roads, aqueducts, and legal system, laid the foundation for modern civilization. The Persian Empire, known for its administrative efficiency and tolerance towards diverse cultures, influenced the governance of future empires. Even though these ancient empires eventually fell, their legacies live on through their contributions to art, architecture, law, and governance.
Avid Writer with invaluable knowledge of Humanity!
Upcoming historian with over 30 million views online.
“You make your own life.”