 or centuries, scientists have been intrigued by the mysteries of Earth’s evolutionary history. Recently, an incredible discovery has shed new light on the origins of life on our planet – a 462-million-year old miniature world containing the fossilized remains of never-before-seen sea creatures! Dubbed as “Tommotian faunas”, these creatures provide an unprecedented insight into the evolution of early life on Earth and are advancing our knowledge of evolutionary history. In this blog post, we will explore what makes this discovery so remarkable, from its features to its implications for understanding early life on Earth. So let’s dive in and uncover some incredible secrets about our distant past!
or centuries, scientists have been intrigued by the mysteries of Earth’s evolutionary history. Recently, an incredible discovery has shed new light on the origins of life on our planet – a 462-million-year old miniature world containing the fossilized remains of never-before-seen sea creatures! Dubbed as “Tommotian faunas”, these creatures provide an unprecedented insight into the evolution of early life on Earth and are advancing our knowledge of evolutionary history. In this blog post, we will explore what makes this discovery so remarkable, from its features to its implications for understanding early life on Earth. So let’s dive in and uncover some incredible secrets about our distant past!
Overview of Discovery
An incredible discovery has recently been made by researchers from the University of Leicester – a 462-million-year old miniature world containing the fossilized remains of never-before-seen sea creatures. This remarkable find provides an unprecedented insight into the evolution of early life on Earth and is advancing our knowledge of evolutionary history.
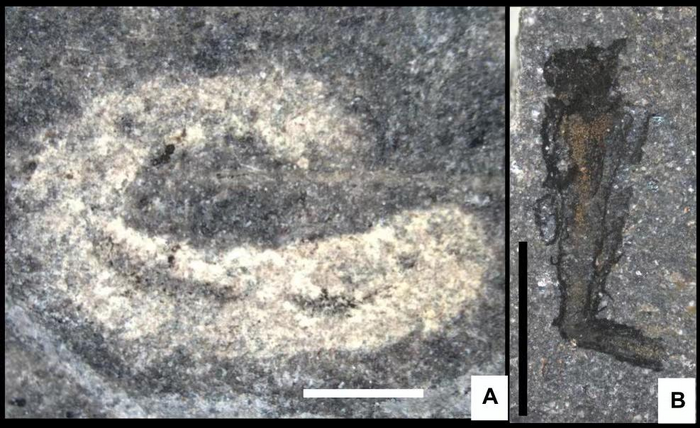

The fossils were recovered from a formation known as Tommotian faunas, and are believed to be the earliest known ancestors of modern clams, snails, squids, and octopuses. The study of these fossils has revealed new information about how different species evolved in their environment and how they responded to changing conditions over time.
What makes this discovery even more remarkable is that it was published in Nature Ecology & Evolution – the top scientific journal for ecology and evolutionary biology research. This high profile publication allows for more people to access this valuable information and provide a platform for further exploration and discussion on this subject matter.
This discovery provides invaluable information about ancient marine life and allows us to explore the origins of specific marine species. It also helps us understand better what conditions could have enabled certain species to evolve over time – giving us an even deeper understanding of life on Earth as we know it today.
What Are Tommotian Faunas?
The Tommotian faunas are an incredible discovery that promises to open new doors in the fields of evolutionary biology and paleontology. These fossils provide a window into life on Earth millions of years ago, and they represent a crucial step in uncovering the history of our planet. By studying this remarkable fossilized collection, scientists can gain valuable insights into how animal life has evolved over time and identify potential patterns in the development of species.
Features of the 462-million-year Old Sea Creatures
The recent discovery of a 462-million-year old fossilized collection of miniature sea creatures is an incredible example of preservation and evolution. The fossils were found in volcanic ash, which allowed for an unprecedented level of insight into the development of early life on Earth.
This unique collection includes over 130 species, most of which are arthropods measuring between 1.5 to 3 millimeters in size. Scientists have identified certain characteristics that make them different from modern species, such as their segmented bodies with jointed limbs – a trait not seen in today’s aquatic animals.

By studying this fossilized set, researchers can gain valuable knowledge into how animal life adapted over time and even identify potential patterns in the development of species. This provides more room for exploration and discussion on this subject matter, allowing us to further advance our understanding of evolutionary history.
In addition to offering this insightful window into our past, these findings also provide evidence that modern clams, snails, squids and octopuses evolved from much simpler forms millions of years ago – known as Tommotian faunas. To ensure everyone has access to this important information, it was published in Nature Ecology & Evolution for other researchers to build upon through future initiatives.
Overall, this incredible discovery offers an exciting opportunity to explore the origin and evolution of certain marine species through a remarkable glimpse into the past – giving us a better idea about how life developed on Earth many centuries ago.
Implications for Understanding Early Life On Earth
This remarkable fossil collection from 462 million years ago offers a wealth of information about the evolution of life on Earth. By studying these ancient species, we can gain insight into how different creatures adapted to changing environments and develop theories for the emergence of complex organisms. Furthermore, this discovery provides valuable data that could help us to predict future trends in animal population adaptation and support conservation efforts around the world.
How This Discovery Is Advancing Our Knowledge Of Evolutionary History

The discovery of a 462-million-year old miniature world containing the fossilized remains of never-before-seen sea creatures is providing an invaluable insight into evolutionary history. The fossils, from a formation known as Tommotian faunas, are believed to be the earliest known ancestors of modern clams, snails, squids and octopuses. This provides crucial evidence that these species evolved from much simpler forms millions of years ago. The findings published in Nature Ecology & Evolution have opened up access to this valuable information to everyone, allowing for further exploration and discussion on the topic.
The fossil collection can also provide insight into the origins of specific marine species and how they responded to changing conditions over time. By studying these ancient creatures, scientists can better understand the conditions under which certain species evolved and gain a greater appreciation for how animal life has adapted over time. Furthermore, by identifying patterns in the development and evolution of different species, researchers can form theories about future trends in population adaptation and conservation efforts around the world.
The discoveries made at Tommotian faunas are helping us to build up an ever more accurate timeline of our planet’s evolutionary history. These findings can also be used to track global environmental changes throughout Earth’s history by looking at how early life adapted or perished due to external factors like climate change or catastrophic events such as asteroid strikes or volcanism. It may even help us gain new perspectives on current day ecological conservation strategies that involve protecting rare organisms from extinction before it is too late.
This discovery offers a unique glimpse into early life on Earth and is advancing our knowledge of evolutionary history in many ways. As more research is conducted on ancient fossils like these, we may uncover even more exciting revelations about the origins and timeline of animal life on our planet – proving yet again just how extraordinary nature truly is!
Avid Writer with invaluable knowledge of Humanity!
Upcoming historian with over 30 million views online.
“You make your own life.”





