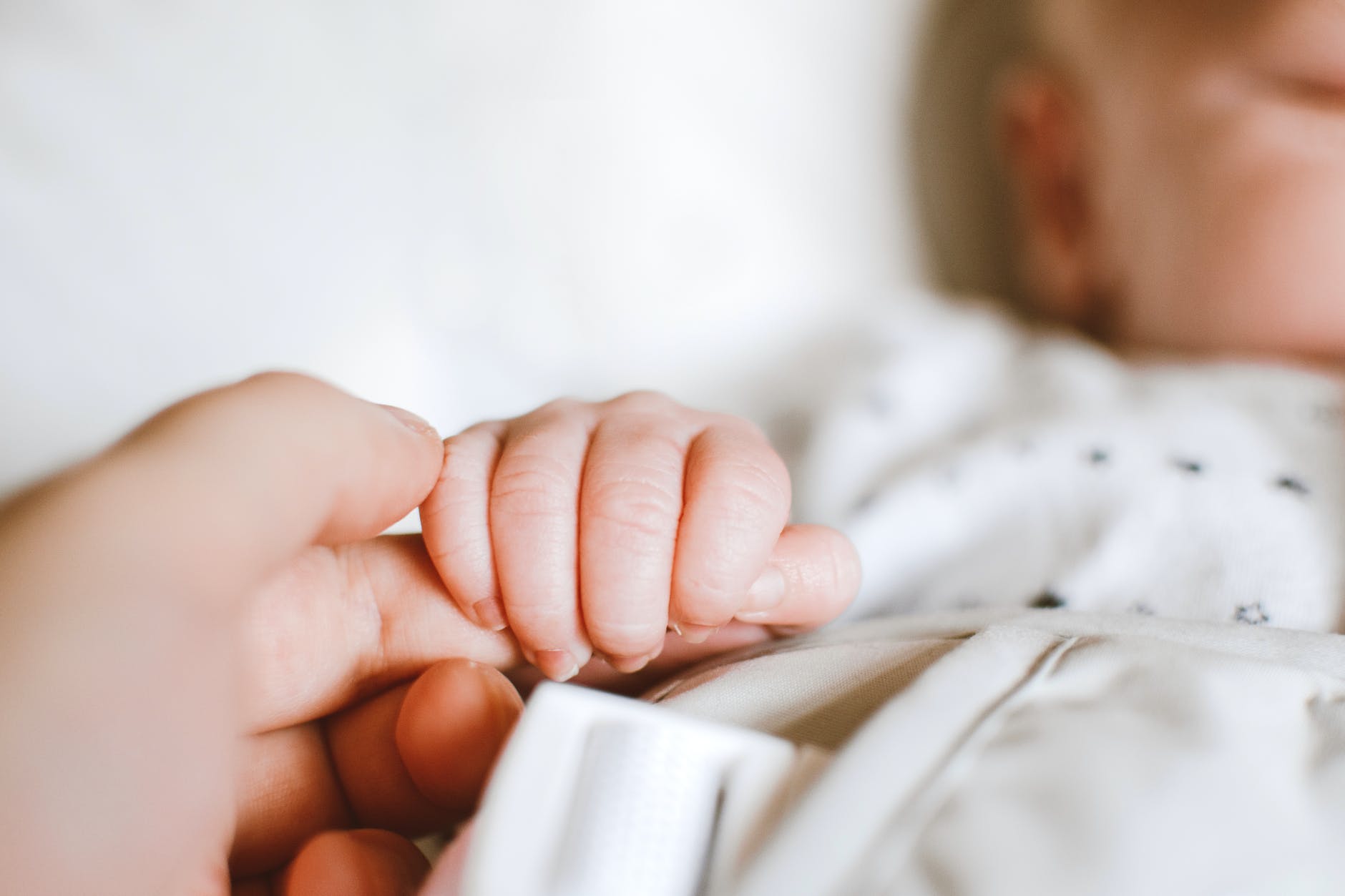
 he world is facing a silent crisis that threatens the very foundation of our societies: the alarming decline in global birth rates. Across continents and cultures, the number of children being born has plummeted to unprecedented levels, raising concerns about the implications for our future. In this article, we explore the factors contributing to this decline, the potential consequences on various aspects of society, and the need for urgent attention to address this pressing issue.
he world is facing a silent crisis that threatens the very foundation of our societies: the alarming decline in global birth rates. Across continents and cultures, the number of children being born has plummeted to unprecedented levels, raising concerns about the implications for our future. In this article, we explore the factors contributing to this decline, the potential consequences on various aspects of society, and the need for urgent attention to address this pressing issue.
Uncovering the Global Plunge
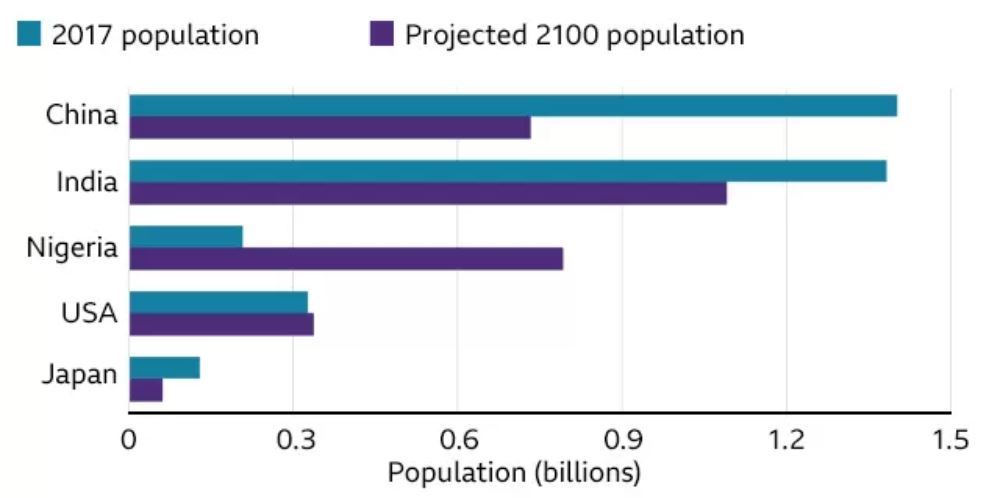
The decline in global birth rates is a phenomenon observed in countries across the world. A recent study by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation revealed that fertility rates have dropped dramatically, with nearly half of all countries experiencing a “jaw-dropping” decline. This shift is not limited to any particular region or socioeconomic group but is rather a global trend that demands our attention.
Numerous factors contribute to the declining birth rates. One significant aspect is the shift in societal dynamics and changing demographic patterns. As countries become more urbanized, individuals are prioritizing careers, education, and personal aspirations, often leading to delayed marriages and childbearing. Economic pressures, increasing costs of living, and limited access to affordable childcare further discourage couples from having children.
Advancements in reproductive technologies have also played a role in the decline of birth rates. As more individuals and couples turn to assisted reproductive techniques, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), the focus shifts from natural conception to medical interventions. While these technologies offer hope to those struggling with fertility issues, they contribute to a decrease in overall birth rates due to the lower success rates and limited availability of these procedures.
Implications for Society
The declining birth rates have far-reaching implications for economies worldwide. With fewer children being born, countries may face challenges in sustaining their labor forces, leading to potential shortages and gaps in the workforce. The aging population exacerbates the strain on social welfare systems, healthcare, and pension schemes, as fewer working-age individuals contribute to supporting the elderly.

The societal consequences of declining birth rates are profound. As populations age, family structures change, and the dynamics of communities shift. There is a potential for a reduced sense of community and support systems, as smaller families and fewer children mean fewer connections and intergenerational relationships. The cultural fabric of societies could undergo significant transformations as the younger generations become a minority.
While the decline in birth rates may have positive implications for environmental sustainability, it also poses unique challenges. With fewer individuals, there may be a decline in consumption patterns, leading to decreased economic growth. Additionally, low birth rates could result in reduced innovation and a loss of human capital, affecting long-term sustainable development goals.
Addressing the Crisis
To address the alarming decline in global birth rates, governments and policymakers must prioritize proactive measures. This includes implementing supportive family-friendly policies, such as affordable childcare, parental leave, and flexible work arrangements. Creating an environment that enables individuals to balance work and family life is crucial in encouraging couples to have children.
Raising awareness about the consequences of declining birth rates is vital. Educational campaigns highlighting the benefits of having children, promoting family values, and debunking myths surrounding parenthood can help shape public perception. Providing accurate information about reproductive health and options for fertility support can empower individuals to make informed decisions.

Building strong community support systems is essential to counteract the challenges posed by declining birth rates. Encouraging intergenerational connections, fostering social cohesion, and investing in programs that promote family-friendly environments can help create a sense of belonging and alleviate the potential negative consequences of shrinking populations.
The silent crisis of declining birth rates demands immediate attention from governments, policymakers, and society at large. The profound implications on economies, communities, and the environment necessitate proactive measures to reverse this trend. By addressing the underlying factors contributing to the decline and implementing supportive policies, we can create an environment that promotes both personal aspirations and a sustainable future for generations to come. It is only through collective efforts that we can ensure a thriving society for the years ahead.
Avid Writer with invaluable knowledge of Humanity!
Upcoming historian with over 30 million views online.
“You make your own life.”





