 umer (Sumeru in Akkadian) was a civilization that flourished in the 3rd millennium BC. The main reason that facilitated the development of Sumer was the very fertile soil between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, this civilization occupying southern Iraq today. At that time, the two rivers formed at the Persian Gulf flow deltas branched with a significant flow. Having abundantly the main human resource, food, the Sumerians were able to develop a prosperous civilization from all points of view. Even so, the maintenance of civilization required a sustained effort on the part of the inhabitants, as there were many obstacles, which made the daily life of the Sumerians difficult.
umer (Sumeru in Akkadian) was a civilization that flourished in the 3rd millennium BC. The main reason that facilitated the development of Sumer was the very fertile soil between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, this civilization occupying southern Iraq today. At that time, the two rivers formed at the Persian Gulf flow deltas branched with a significant flow. Having abundantly the main human resource, food, the Sumerians were able to develop a prosperous civilization from all points of view. Even so, the maintenance of civilization required a sustained effort on the part of the inhabitants, as there were many obstacles, which made the daily life of the Sumerians difficult.
The life of a common man from Sumer
Religion was the main influencer in the Sumerian society, and this thought imposed the standards in all aspects of life, “the Sumerians believed that they were surrounded by countless gods, spirits, demons, good or bad geniuses who mingled in their daily lives and depended on their fate. them. ”(Constantin Daniel in the Sumerian Civilization, Sport-Tourism Publishing House, 1988). Also, the relationship with the gods was totally submissive, and their perception was that humans were created to serve the gods, thus diminishing, in the Sumerian view, the role of man in the universe.
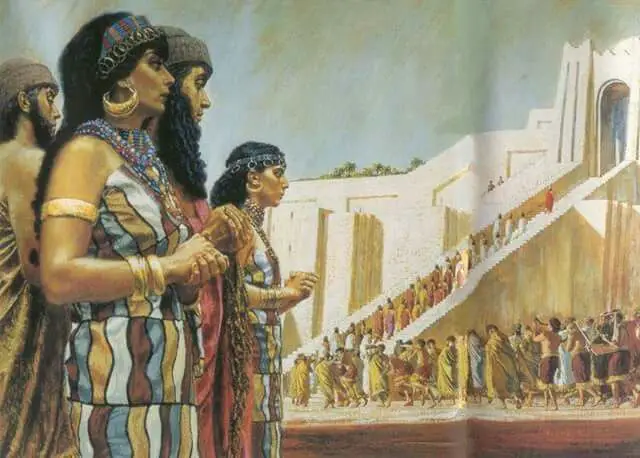
Although the Sumerians had urban settlements, they had an agricultural base, because, being forced to maintain the canals, a significant labor force was needed. Another reason why the Sumerians preferred this system was because of the frequent floods they were getting. However, the most important reason lies in the nomadic invasions of the desert or of the mountains that were to plunder and destroy these settlements, so the Sumerians were forced to erect fortifications, at the shelter where their homes were located. Thus, a city consisted mainly of the houses of the inhabitants, the temple, a market, and the granary.

They were surrounded by a thick wall with rooms for the soldiers. For example, the fortifications of the city of Uruk, built around 2000 BC, consist of a double wall, the main wall is 4–5 meters thick, with a total length of 9, 5 km, protected by about 800 towers, with gates only to the north and south. It is easy to imagine that the erection and maintenance of the fortifications involved the hard work of the inhabitants, and with the imposition of these limits the city could not expand if the population increased, so the inhabitants, as the city developed, it became more and more crowded.
The house of ancient Mesopotamia was built of bare bricks, reeds, mats and few planks of wood, which from the fourth-millennium had acquired a typical form, which had remained for several millennia and had not changed at all in the historical times, is much like the Arab dwellings in the villages of today’s Iraq. It should be added that these constructions had narrow rooms and entrances, with the Sumerians having the motto that if the gates of a house are tight the welfare will be master there, and it will make a rich profit.

Since the wood was hard to get and very expensive, the tenants came with their gate when they rented a house. Also, due to the fact that the wood was rare, the furniture was poor, being mainly made of reed. In the kitchen, there were brass pots, clay pots, jugs, cups, etc., and on the floor were sheep wool rugs, because this material was abundant in Sumer, and these confections showed the craftsmanship of the Sumerian weavers. There was also the statue of the protective god of the house next to a clay sacrificial, and besides it the exterior walls of the houses were painted with asphalt, but also with red stripes, this being the color that drove away from the demons.
Relationships between Sumerians
For Sumerians, the family was very important, being considered, as in the present day, the foundation of the society. Just as the king was ruler over the city-state, so was the father/husband king over his house. The marriage was monogamous, and the woman, unlike other societies of that time, had more freedom, as in the Sumerians the role of mother was crucial. Being very high infant mortality due to lack of hygiene, the woman had to give birth to as many children as possible. As for the holidays, everyone took part in them, and on these occasions, any social difference was erased, and there were also processions that ended with orgies.

Occupations
Sumerian cities had to import many raw materials, as a marshy plain area did not allow them a great variety of products, but they had a surplus of food, especially cereals. Thus, trade became important, this being a reason for the development of cuneiform writing, and here we can see the first forms of bureaucracy to have control over the routes, it needed clear registers, contracts, and laws regarding the transport of goods. Therefore, the school became indispensable also for the children who were to become traders.
The staple food was bread made from barley flour eaten with dairy and greens. There was only one hot meal a day, which consisted mainly of flour, fish and a variety of vegetables. The meal was taken twice a day, in the morning and in the evening. The reason for not eating at lunch is that people were busy at that time of day with daily tasks. Meat, apart from fish, was only eaten on special occasions (holidays), because goat, sheep, camel or beef was rarely found, but pork was consumed more often. Also, the Sumerians raised birds, mainly chickens.
Crisis
Of course, the hardships of living in Sumer were significant, but they could reach paroxysm during times of war, drought or tyrannical regimes. Through the Sumerians and through these periods, history shows us a dark part of man where the only law that remains standing is that of survival and in which, in a starving, besieged city, the mother was cooking a child to feed the rest of the family. Then, after the population of the city was weak enough, the enemy army would enter the city and massacre all the inhabitants. One thing to note is that Sumerian cities often fought with each other, as was the case with King Eannatum, who extended his rule in Lagash over all Sumerian cities.
Avid Writer with invaluable knowledge of Humanity!
Upcoming historian with over 30 million views online.
“You make your own life.”





