 omets, asteroids, and supervolcanoes can have huge impacts on life on Earth, such as five mass extinctions in the past caused by sudden ice ages and drastic changes in the water and atmosphere. The only thing scientists disagree on is which of the three, a comet, an asteroid, or a supervolcano, caused which mass extinction and whether it was perhaps a combination of all these and other unknown factors.
omets, asteroids, and supervolcanoes can have huge impacts on life on Earth, such as five mass extinctions in the past caused by sudden ice ages and drastic changes in the water and atmosphere. The only thing scientists disagree on is which of the three, a comet, an asteroid, or a supervolcano, caused which mass extinction and whether it was perhaps a combination of all these and other unknown factors.
But this was all long before the Cenozoic, which began with an asteroid impact that wiped out the dinosaurs and left the birds behind to make way for a new species, humans. The neediest species. A few millennia fast-forward into another climate change, and more and more people are panicking that humans have caused their own extinction.
Scientists argue that the current extinction rate of life on Earth caused by human activities and global temperature rise, while high and worrying, does not qualify as a mass extinction under current parameters and will not do so in the near future.
The first two mass extinctions changed life on Earth forever
The first extinction occurred 444 million years ago in the Paleozoic era and resulted in the disappearance of 85% of all marine species as a result of global cooling, glaciation, and falling sea levels. Glaciation forced species to adapt to colder conditions first, and later, when the ice melted, the survivors had to adapt again to the new composition of the atmosphere. The cause of glaciation is not fully understood, however, because it occurred so long ago that the ocean floor and continents changed in more than one way.
The most popular theories range from supervolcanoes to chondrite meteors to a gamma-ray burst from a supernova that tore a large hole in the ozone layer.
The second extinction occurred in the late Devonian period, now known as the Age of Pisces, 372 million years ago. 86% of all life on Earth was wiped out. Most life was in the sea, and the colonization of the land had only begun with the first plants and insects that colonized the solid ground. Because herbivorous animals on the land were still far in the future, the plants grew so much that they probably reduced the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, which led to global cooling.
Scientists do not know what happened during the two Chataclysms, the Kellwasser event and the Hangenberg event, which occurred several million years apart. At that time, a 32-mile-wide crater formed in Sweeden, possibly indicating a meteorite impact. And two other impacts occurred during this one million-year period. There is also the possibility that a nearby supernova and/or Siberian supervolcano reduced the ozone in the atmosphere.
The Biggest Mass Extinction or the Great Dying was caused by volcanic activity across Siberia
After the Devonian extinction, tetrapods – the ancestors of the first amphibians and later reptiles, birds, and finally mammals – began to dominate the land. Life flourished but tragically ceased when blanket eruptions in Siberia and China darkened the skies, weakened the light, released volcanic dust into the atmosphere, emitted poisonous gases, acidified the oceans, and started a never-ending series of wildfires that burned everything.
The supercontinent of Pangaea began to break up at this time, contributing to a lack of movement in the world’s oceans and creating a global basin of stagnant water that only increased the accumulation of carbon dioxide. The rise in ocean temperatures also led to a decline in oxygen levels in the water.
The Permian-Triassic mass extinction 250 million years ago wiped out large numbers of insect and marine species. It is estimated that 90% of all marine species disappeared, while at least 70% of vertebrates on land became extinct. Many animal species disappeared completely from the fossil record at this time. Land animals took millions of years to recover and take on new forms. Marine ecosystems took four to eight million years to recover.
This extinction lasted about 50,000 years and changed the course of life completely. Climate models predict that the oceans have lost 70% of their oxygen inventory at the time, confirming the climate theory that oxygen loss, together with warming, is the main cause of most species extinctions.
The Rise and Fall of Dinosaurs
History repeats itself. After life recovered one more time and introduced new species such as giant crocodiles and dinosaurs, massive volcanic activity occurred in an area of the world now covered by the Atlantic Ocean called the Mid-Atlantic Magma Province, a large eruptive province in central Pangaea that triggered the sudden extinction of up to 80 % of all land and marine species.
Remains of these ancient lava flows are now scattered across eastern South America, eastern North America, and West Africa. Huge amounts of greenhouse gases warmed the Earth again, causing ice melt, sea level rise, and acidification. But there were winners too. Small mammals, dinosaurs, and their relatives, the crocodylomorphs, whose descendants include today’s crocodiles, exploded in diversity and revitalized the earth.
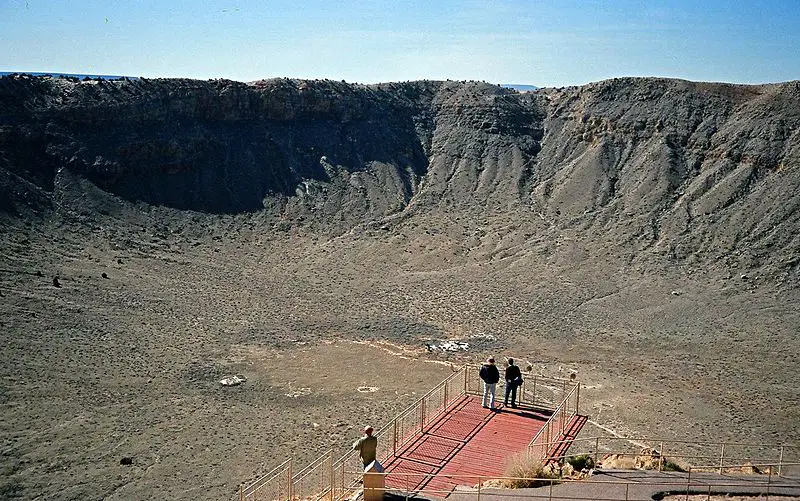
For 135 million years, dinosaurs roamed the lush Earth until it was time to begin a new modern era, the Cenozoic Era, which began with the impact of a large asteroid near Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula, which is very well documented in the date-appropriate geological sedimentary layers around the world, showing a rock layer full of iridium, which isn’t normally found on Earth but gets there with the asteroid.
However, the event coincided with large-scale volcanic activity in the Indian Deccan Trap, which was already underway, and soon all these disasters will cause an ice age and the complete extinction of the dinosaurs, whose last day on Earth began with an asteroid in their direction.
Then came the months when the sky was blackened with asteroids and volcanic debris and dust. The global temperature cooled and a long, dark, freezing winter set in. Plants died out and with them the last dinosaurs that had withstood the unprecedented famine and cold. 76 % of all species on the planet disappeared, and only mammals, some marine species, and birds that evolved from dinosaurs survived into the Cenozoic, the era of humans.
Does all this mean that an asteroid could hit the earth? Sure. And probably NASA can’t do anything about it. But then, who knows what could happen?

Writer and director who thinks different and does everything differently. Art enthusiast. Wandering and wondering. Until the end of meaning.
irena_curik@hotmail.com




